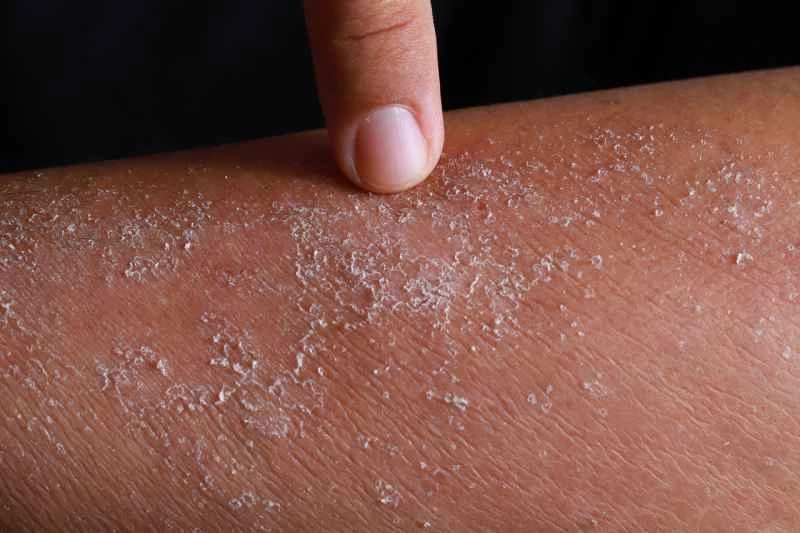
For broken eczema wounds, topical ointments such as fusidic acid ointment, mupirocin ointment, triamcinolone acetonide cream, mometasone furoate cream, and halometasone cream can be applied. If the wound becomes infected or symptoms worsen, seek medical attention as soon as possible to avoid complications.
1. Fusidic acid ointment
Fusidic acid ointment is suitable for use on broken skin caused by skin infections, impetigo, etc. This medication has broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. Avoid contact with eyes and other mucous membranes, such as the mouth and nose, during use.
2. Mupirocin ointment
Mupirocin ointment can be used to treat bacterial skin diseases, including skin infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus. This medication has good antibacterial efficacy against Gram-positive bacteria. Adverse reactions such as burning or stinging may occur when used topically; careful observation and discontinuation of the medication if necessary are required.
3. Compound Triamcinolone Acetonide Cream
Compound triamcinolone acetonide cream is used to relieve symptoms such as itching and redness caused by inflammatory skin diseases such as eczema and dermatitis. Its main ingredients are hydrocortisone and triamcinolone acetonide. Long-term use may lead to side effects such as skin atrophy and pigmentation, and it is not suitable for large-area application.
4. Mometasone furoate cream
Mometasone furoate cream is suitable for various types of allergic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, and hormone-sensitive dermatitis. This product is a topical corticosteroid preparation with anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effects. Long-term use may cause side effects such as skin atrophy and telangiectasia; therefore, it is not suitable for prolonged continuous use.
5. Halometasone cream
Halometasone cream is primarily used to treat chronic inflammatory skin diseases such as psoriasis, neurodermatitis, and seborrheic dermatitis. This product is a potent topical corticosteroid with strong anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effects. Long-term use may cause side effects such as skin atrophy and telangiectasia; therefore, it is not suitable for large-area application.
When using the above medications, patients should keep the affected area clean and dry, and avoid scratching to prevent worsening of the condition. It is also recommended that patients wear loose, breathable clothing to reduce friction and irritation.