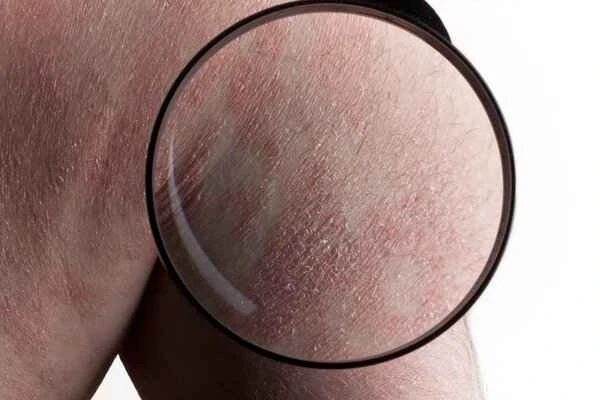
Urticaria (hives) is mainly related to an abnormal immune response. When exposed to certain triggers, the skin releases substances such as histamine, leading to vasodilation and localized edema. If you experience symptoms, it is recommended that you record possible triggers and consult a doctor promptly for a definitive diagnosis.
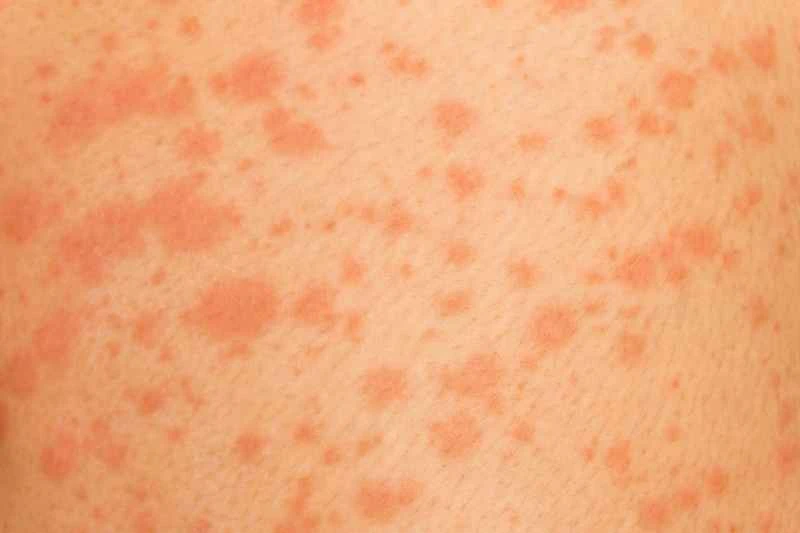
The specific triggers can be categorized as follows:
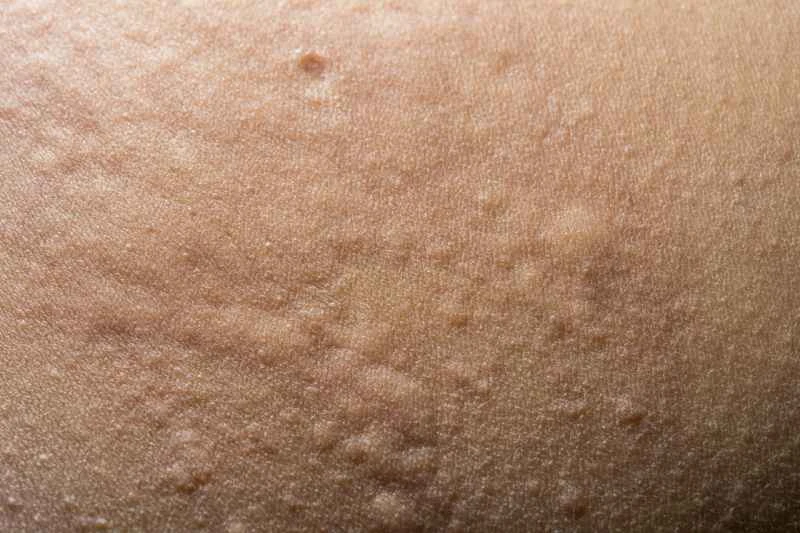
1. Food factors: Some people may experience reactions after consuming seafood, nuts, or foods containing additives.
2. Environmental irritants: Common allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander, or physical factors such as temperature changes and sunlight exposure can all trigger allergies.
3. Infection and Stress: Viral infections such as colds, emotional stress, or fatigue can affect immune status and become potential triggers.
4. Drug effects: Some painkillers, antibiotics and other drugs may also cause allergic reactions.
Daily prevention can start with the details: keep a record of your diet and environmental exposure to help identify personal allergens; wear loose cotton clothing to avoid scratching your skin; if symptoms recur, bring your records to see a doctor, who may help with allergy testing. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and managing stress can also help reduce flare-ups.