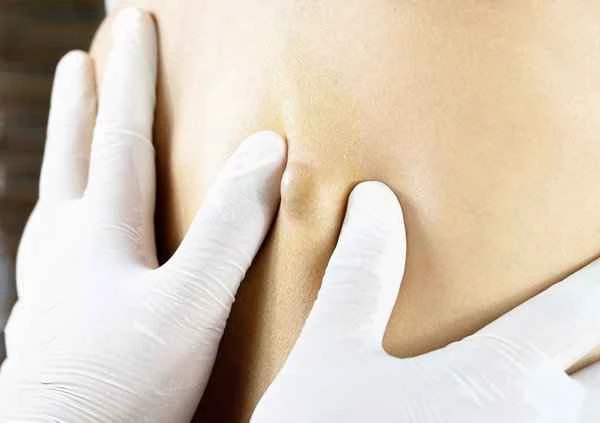
The healing time for urticaria varies from person to person. Acute flare-ups typically subside within hours to weeks, while chronic cases may last for months or even longer. It is recommended to seek medical attention promptly for targeted treatment based on the specific type and cause.
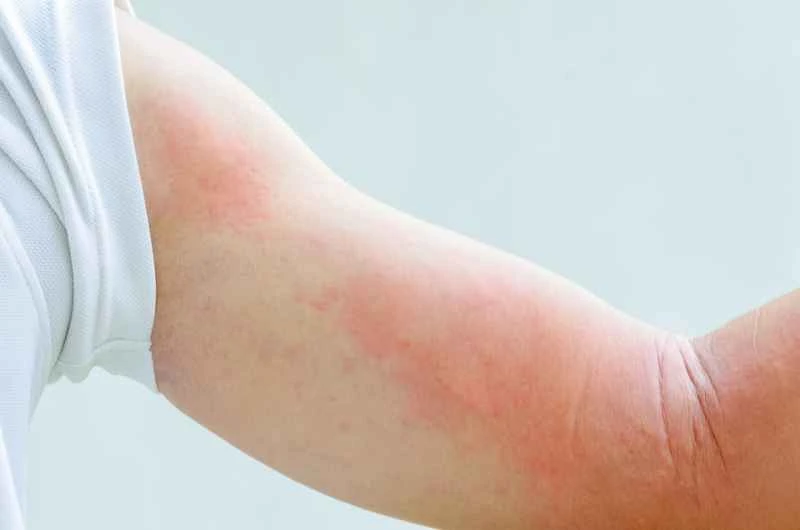
1. Acute urticaria: Most cases are caused by allergies or infections. Symptoms come on and go quickly, usually subsiding within hours to days, and in some cases lasting no more than six weeks. Avoid contact with suspected allergens and use medication as directed by your doctor.
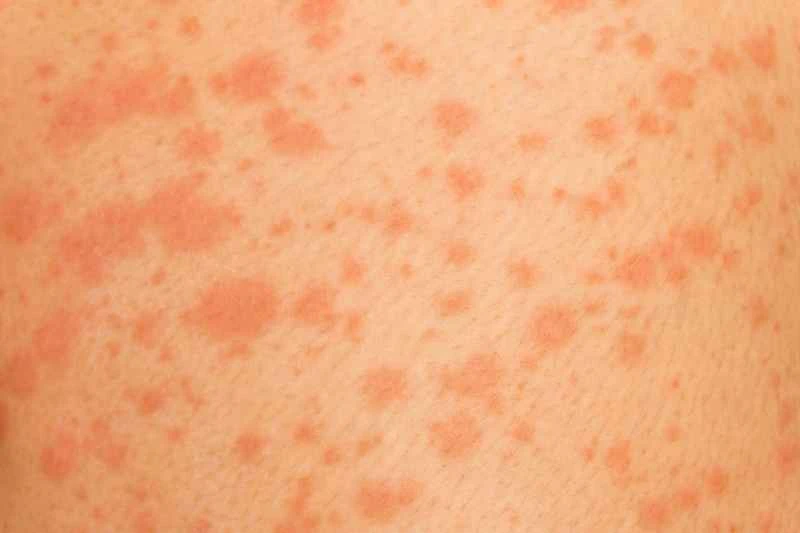
2. Chronic urticaria: Recurrent episodes lasting more than six weeks may be related to immunity, stress, or chronic diseases. Treatment is lengthy, potentially taking months or longer, requiring patience and cooperation with the doctor to adjust the treatment plan and gradually control symptoms.
3. Influence of triggering factors: Recovery speed is related to the clarity of the triggering factor. If the triggering factor (such as food or environmental factors) can be accurately identified and avoided, recovery is often faster; if the cause is unknown, longer observation and management are required.
In daily life, pay attention to recording the pattern of your flare-ups, avoid scratching your skin, and wear loose clothing. If symptoms recur or worsen, please have regular follow-up appointments. Your doctor will adjust the treatment plan based on your recovery progress to help you better manage your condition.