For rapid resolution of urticaria, antihistamines can be considered, but should be used under the guidance of a doctor. The following are common treatment methods and precautions:
1. Commonly Used Oral Medications
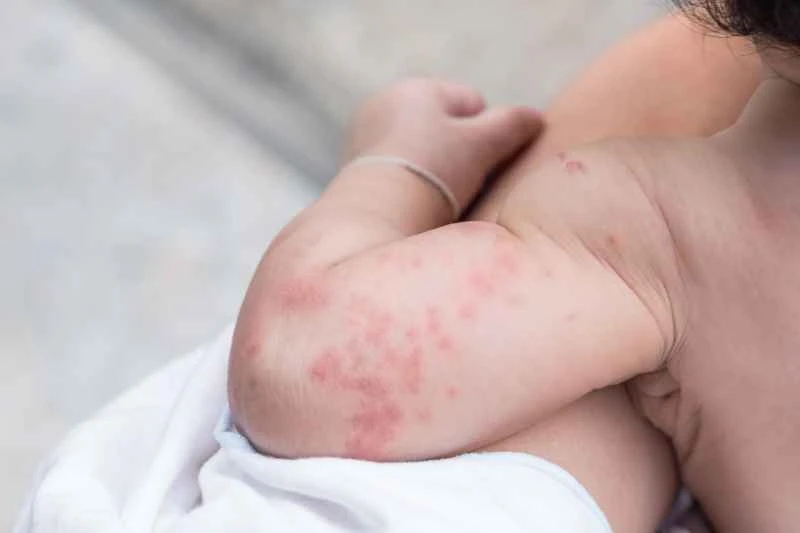
Antihistamines such as loratadine and cetirizine can relieve itching and wheals, usually taken once daily. Some medications may cause drowsiness; it is recommended to adjust the dosage according to the instructions or doctor's prescription.
2. Topical medication as an adjunct
Calamine lotion can be applied to the affected area to temporarily relieve itching, and cold compresses can also help reduce local redness and swelling, but avoid scratching to prevent skin damage.
3. Handling of Special Circumstances
If accompanied by difficulty breathing or facial swelling, seek immediate medical attention, as this may be a severe allergic reaction. For recurrent urticaria, investigate potential triggers such as food or environmental factors.
4. Precautions for medication use
Pregnant women, children, and patients with chronic diseases should consult a doctor before using this medication. Avoid mixing medications on your own to prevent overlapping or interactions of ingredients.
Keep a daily record of your diet and activities during flare-ups to help identify triggers. During acute flare-ups, it is recommended to wear loose-fitting cotton clothing and reduce exposure to spicy foods. If symptoms persist for more than a week or recur frequently, consult a dermatologist promptly to develop a long-term management plan.


