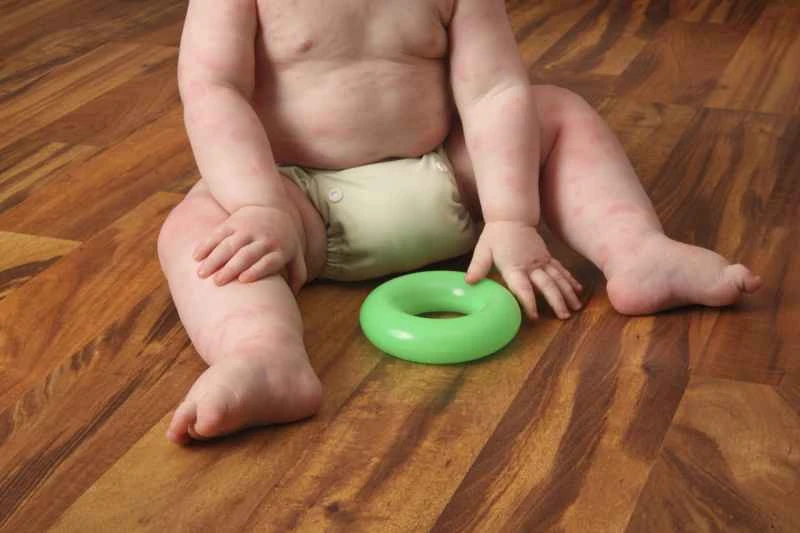
Some cases of urticaria may resolve on their own, but the recovery time varies from person to person, typically ranging from several hours to several weeks. It is recommended to closely monitor changes in symptoms, and if they recur or worsen, consult a doctor to determine the cause.

1. Acute urticaria: Most cases are caused by allergies or infections. Symptoms may last from several hours to several days, and in some patients, they may gradually subside within 1-2 weeks.
2. Chronic urticaria: Symptoms recur for more than 6 weeks, and the possibility of spontaneous remission is low. It often requires a long period of conditioning or intervention.
3. Influence of triggering factors: If the symptoms are caused by short-term factors such as food or drugs, they may be relieved quickly after the triggering factor is removed; if they are related to immunity or chronic diseases, the recovery time may be prolonged.
Daily routines can help identify potential triggers by tracking your diet and environmental exposure. Avoid scratching your skin, and wear loose-fitting cotton clothing to reduce irritation. If the rash spreads or is accompanied by discomfort such as difficulty breathing, seek medical attention promptly.


