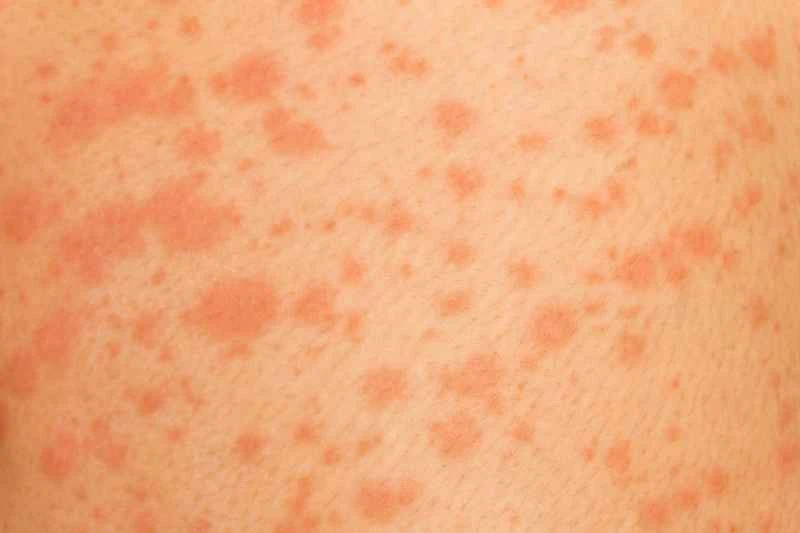
Urticaria (hives) is usually not a precursor to a serious illness; in most cases, it's a common skin allergic reaction. We suggest you observe any changes in your symptoms first, and seek medical attention promptly if other abnormal symptoms appear.
1. Common causes analysis: Most cases of urticaria are related to food, drug allergies, or environmental irritants. For example, seafood and pollen can trigger wheals and itching on the skin. These conditions can usually be relieved by avoiding contact with allergens or by simple treatment.
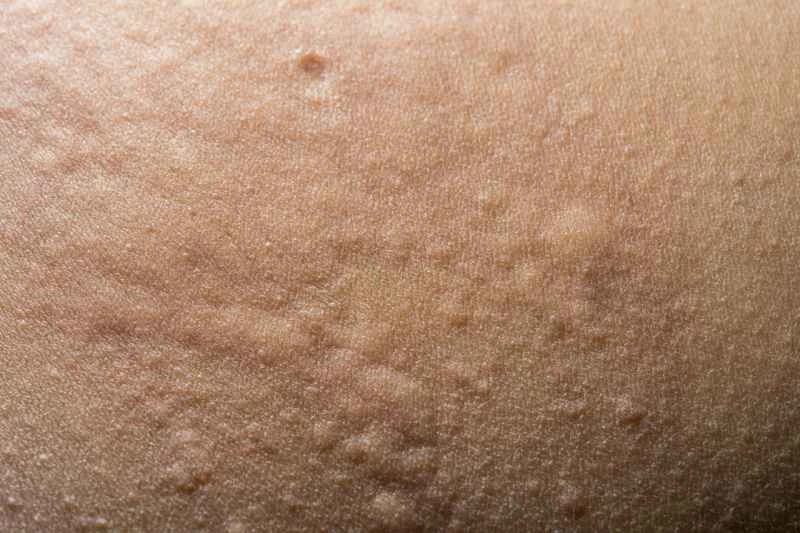
2. Situations requiring attention: In rare cases, recurrent or severe urticaria may be related to immune system dysfunction. If symptoms such as fever, joint swelling and pain, or difficulty breathing occur at the same time, a systemic examination is recommended.
3. Daily coping methods: Recording dietary and environmental factors during an attack can help identify the triggers. Wearing loose cotton clothing and avoiding scratching can reduce discomfort. Applying cold compresses can also temporarily relieve itching.
It is recommended to maintain a regular daily routine and reduce the impact of mental stress on the body. If the rash persists for more than 6 weeks or recurs, you can go to the dermatology department for allergen testing; in case of emergencies such as a tight throat or chest tightness, you should seek medical attention immediately. You can keep anti-allergy medication on hand for emergencies, but it is best to consult a doctor before use.