Treatment for urticaria usually requires medication under the guidance of a doctor. Common options include antihistamines and hormone medications, but the specific medication should be determined based on the severity of the condition and individual circumstances. Do not self-medicate.
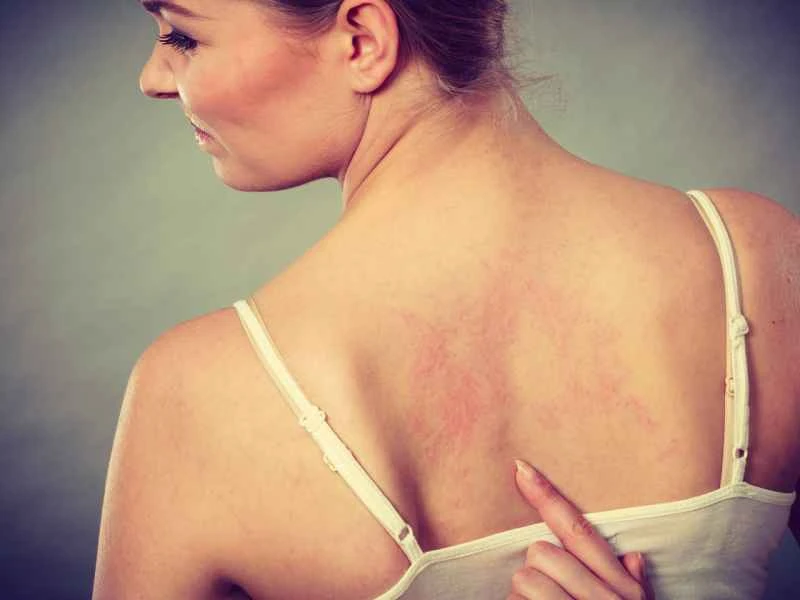

1. **Common medications for mild symptoms**: If the rash is small and the itching is not severe, doctors often recommend oral antihistamines, such as loratadine or cetirizine. These medications can help relieve itching and reduce wheals.
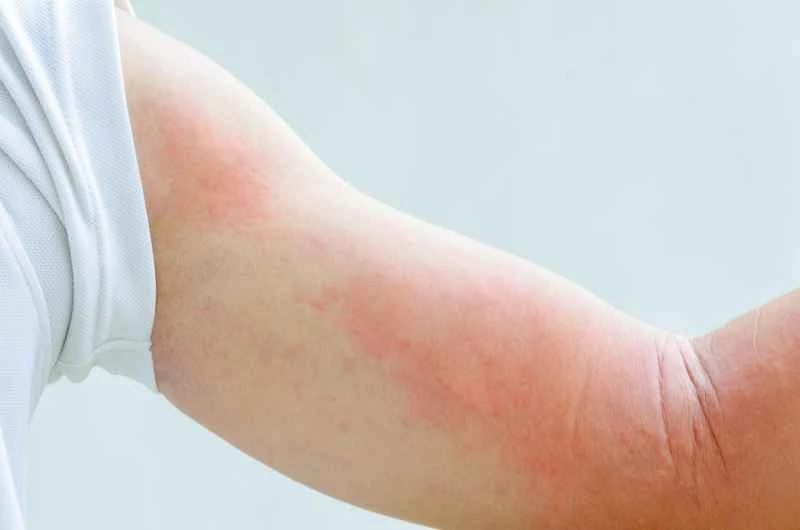
2. **Medication for Moderate to Severe Cases**: If the rash is widespread, recurrent, or accompanied by significant discomfort, short-term use of steroid medications, such as prednisone, may be necessary to quickly control the inflammation. Sometimes, immunosuppressive drugs may also be used in conjunction.
3. **Special Circumstances Management:** Some patients may experience allergic reactions and should avoid contact with the allergen. If severe reactions such as difficulty breathing occur, immediate medical attention is required, and emergency administration of adrenaline may be necessary.
It is recommended to first consult a dermatologist for an evaluation and to prescribe appropriate medication. At the same time, carefully record factors such as diet and environment during flare-ups to help identify possible triggers. Maintaining a regular lifestyle and avoiding scratching can help support treatment and reduce recurrence.