Vitiligo (leukoderma) is a common skin disease characterized by loss of pigmentation. Currently, there is no specific treatment and it is generally not completely curable.

The pathogenesis of vitiligo is not fully understood, but it may involve multiple factors, including genetics, autoimmunity, and neuropsychiatric factors. These factors may lead to melanocyte dysfunction or destruction, resulting in skin depigmentation. Due to the complexity of the causes of vitiligo, current treatments mainly focus on alleviating symptoms by regulating the immune system and promoting melanocyte regeneration, but they cannot completely cure the disease. Patients should seek professional medical help promptly after diagnosis to control the progression of the disease.
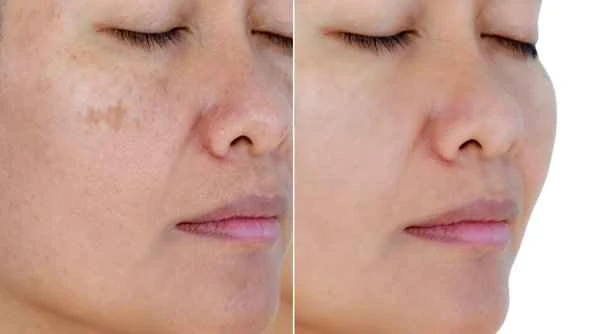
Because the causes of vitiligo are complex, it is difficult to find a single effective treatment. A personalized treatment plan usually needs to be developed by comprehensively considering the patient's individual differences and the severity of the condition.
Patients should avoid using strong cosmetics or other chemicals, as these may worsen their condition. They should also take precautions against sun exposure to reduce ultraviolet (UV) radiation, as UV rays may trigger or exacerbate vitiligo symptoms.
For vitiligo patients, it is recommended to have regular follow-up visits, follow the doctor's treatment advice, and maintain good lifestyle habits and a positive attitude, which will help control the progression of the disease.