The difference between a boil and a tumor is that the former is a local skin inflammation caused by bacterial infection, while the latter is a lump formed by abnormal cell proliferation.
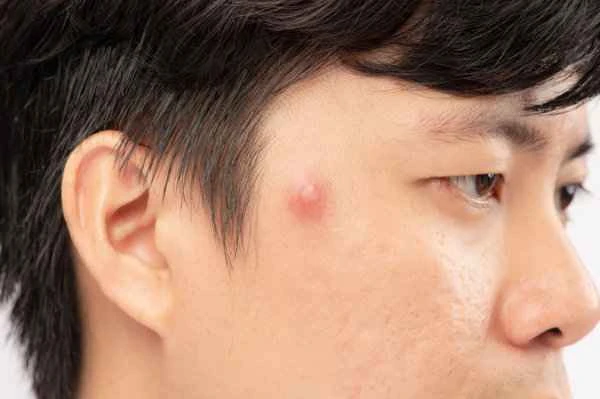
Understanding the difference between boils and tumors is crucial, as it helps us take timely and appropriate medical action, avoiding misdiagnosis and delayed treatment. Differentiating between them allows us to manage and treat these conditions more effectively, thereby reducing pain and complications.
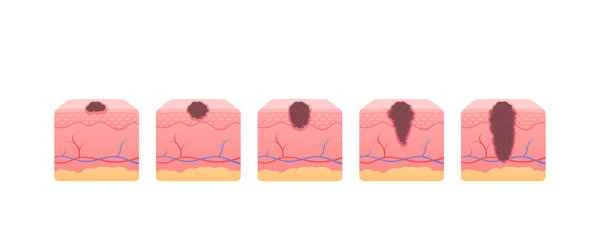
Boils and tumors differ significantly in their causes, symptoms, and treatments. Boils are usually caused by bacterial infections such as Staphylococcus aureus, presenting as localized redness, swelling, pain, and pus formation. Tumors, on the other hand, result from uncontrolled cell growth, leading to abnormal proliferation. They can occur anywhere in the body and present with a variety of symptoms, ranging from asymptomatic to painful lumps. Boils are typically treated with local heat application, antibiotics, or incision and drainage, while tumor treatment is more complex and may require a combination of therapies including surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy.
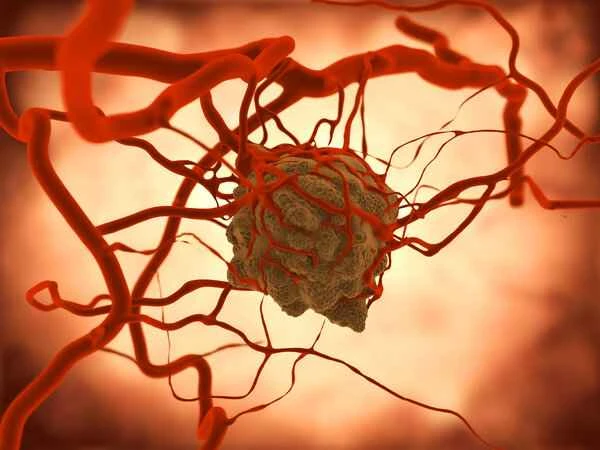
After understanding the difference between boils and tumors, we should learn to observe any abnormal changes in our bodies and seek medical attention promptly. When faced with redness, swelling, and pain on the skin, if the symptoms are mild and localized, it may be a boil, which can be relieved with simple home care and antibiotic treatment under the guidance of a doctor. If symptoms such as persistent lumps, worsening pain, or weight loss occur, a tumor should be highly suspected, and medical attention should be sought as soon as possible for further examination and treatment. It is important that any suspected symptoms should be promptly addressed by a professional doctor for diagnosis and treatment; never attempt to diagnose or treat yourself.
【Useful Tips:】
1. Pay attention to any abnormal changes on the skin, such as redness, swelling, or pain.
2. For persistent lumps or unexplained weight loss, seek medical attention promptly.
3. Avoid self-medicating before a diagnosis is made, so as not to delay treatment.
4. Have regular physical examinations, especially for people with a family history of cancer.


