Scar pregnancy is an ectopic pregnancy that occurs at the site of a previous cesarean section incision scar. Treatment requires different measures depending on the specific circumstances of the patient.
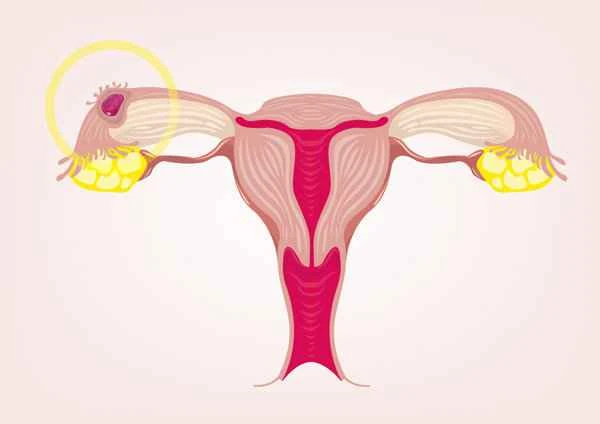
Treatment of cesarean scar pregnancy first requires a definitive diagnosis, confirmed by ultrasound examination to determine the location of the pregnancy and the development of the embryo. The primary principle of treatment is to terminate the pregnancy while preserving the uterus as much as possible to avoid serious complications such as massive bleeding. Treatment methods mainly include medication, surgery, and interventional therapy. Medication primarily uses methotrexate to terminate the pregnancy by inhibiting cell growth; this is suitable for early-stage cesarean scar pregnancies with small embryos. Surgical treatment includes hysteroscopic and laparoscopic procedures, suitable for cases where medication is ineffective or unsuitable. Interventional therapy involves injecting medication into the uterine artery via a catheter to achieve a local treatment effect; this is suitable when medication and surgery are ineffective. The selection and application of these treatment methods should be based on a comprehensive consideration of the patient's specific circumstances, such as the location of the pregnancy, the size of the embryo, and the patient's general condition, to achieve the best treatment outcome.

When treating cesarean scar pregnancy, it is crucial to be aware that the treatment carries higher risks, including severe complications such as massive bleeding and uterine perforation. Treatment often requires multidisciplinary collaboration, involving obstetrics and gynecology, interventional radiology, and radiology departments to ensure safety and effectiveness. During treatment, patients need to actively cooperate with the doctor's treatment plan and maintain a positive attitude, avoiding excessive anxiety and stress, as these factors positively impact treatment outcomes and recovery.
[Management Tip:]
1. Have regular ultrasound examinations to monitor the location of the pregnancy and the development of the embryo.
2. Follow your doctor's instructions and take medication or undergo surgical treatment as prescribed.
3. If you experience any abnormal symptoms such as abdominal pain or vaginal bleeding, you should seek medical attention promptly.


