The recovery time for postoperative scar adhesion rupture varies from person to person, and usually takes from several weeks to several months.
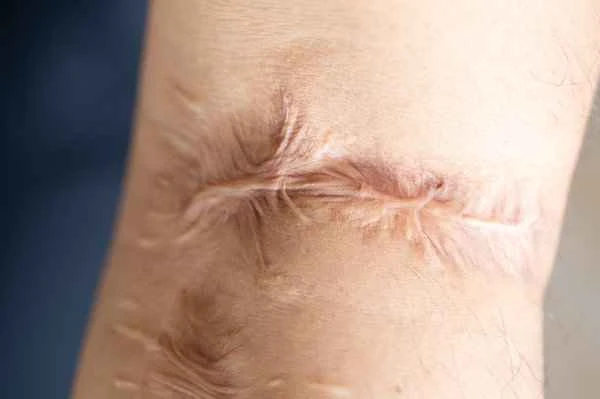
Recovery from postoperative scar adhesion rupture is influenced by a variety of factors, including the severity of the rupture, the individual's healing ability, the presence of infection, and the treatment measures taken. In the early stages of rupture, doctors typically perform debridement to remove necrotic tissue and reduce the risk of infection. Subsequently, the ruptured area is covered to promote healing, and sometimes biomaterials or skin grafts are used to accelerate the recovery process. During the healing process, keeping the wound clean, avoiding strenuous exercise, and following medical advice are crucial. Nutritional status and blood circulation also affect the recovery speed; a proper diet and adequate rest are equally important for promoting wound healing.
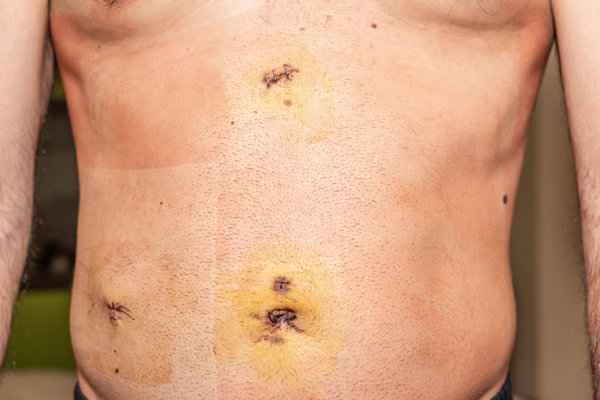
In managing postoperative scar adhesion rupture, patients may encounter some risks and misconceptions. For example, some patients may mistakenly believe that the healing speed is directly proportional to the degree of pain, thus ignoring potential infections or other complications. In reality, pain is not always a sign of healing; sometimes it may be a signal of infection or other problems. Timely communication with the doctor and undergoing necessary examinations and treatments are key to avoiding potential risks.
[Management Tip:]
1. Change dressings regularly and keep the wound clean.
2. Avoid strenuous exercise to reduce stress on the wound.
3. Seek medical attention promptly if symptoms such as redness, swelling, or fever occur.


