Vulvar shingles typically causes itching. Vulvar shingles is a skin infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). This virus initially causes chickenpox, and may then remain dormant in nerve tissue, reactivating when immunity weakens, leading to shingles. When shingles appears in the vulvar area, patients often experience symptoms such as itching, pain, and burning.
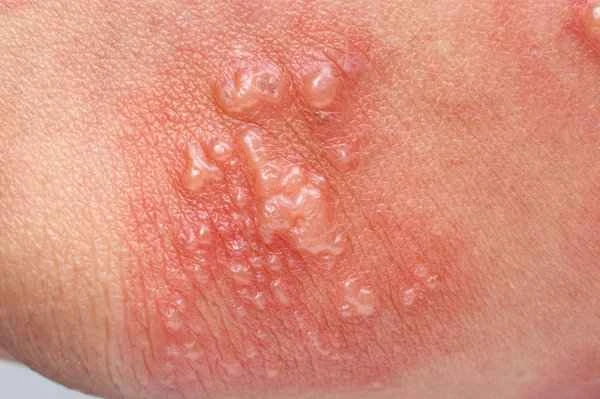
The itching associated with shingles is caused by an inflammatory response triggered by the virus activating neurons. When the virus becomes active again, it travels along nerve fibers to the skin's surface, causing erythema, blisters, and discomfort such as itching and pain. This itching is a typical symptom of shingles, usually starting within a few days of the rash appearing and potentially lasting throughout the course of the disease.
The itching associated with shingles can vary from person to person; some may experience mild itching, while others may experience severe itching. Itching may also be accompanied by other symptoms such as pain and burning sensations, the severity of which also varies from person to person. In treating shingles, in addition to treating the virus itself, measures need to be taken to relieve itching and other discomfort.
[Management Tip:]
1. Use antiviral medications recommended by your doctor, such as acyclovir, to control viral replication.
2. Use antipruritic creams or oral antihistamines to relieve itching.
3. Keep the affected area clean and dry, and avoid scratching to prevent secondary infection.


