Treatment for eczema requires selecting medication based on its type and severity. Topical ointments used under a doctor's guidance usually provide quick relief. It is recommended to consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis to avoid delaying treatment by self-medicating.
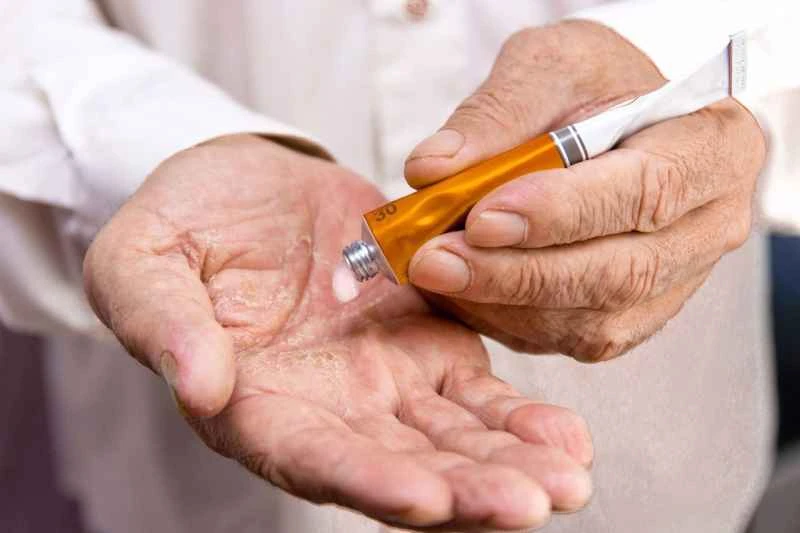
1. Mild eczema: Use moisturizing cream regularly to keep the skin hydrated. If redness, swelling, and itching occur, the doctor may recommend using a mild steroid cream, such as hydrocortisone, to help reduce inflammation.
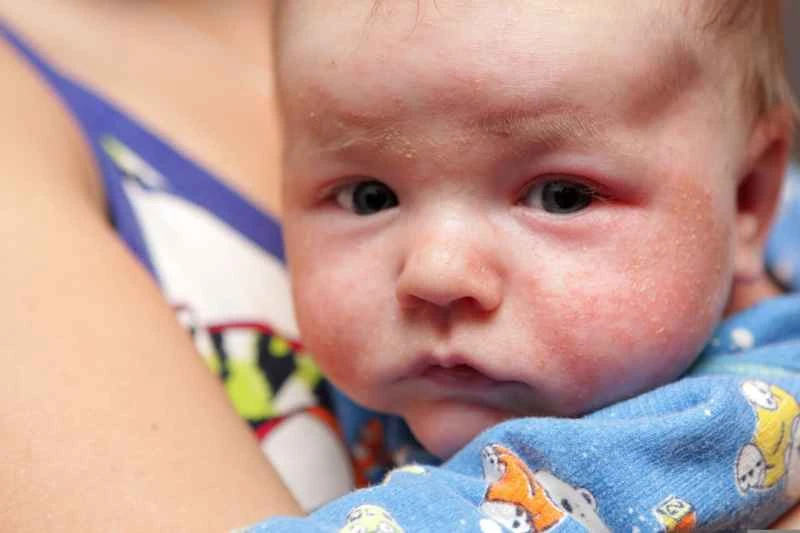
2. Moderate eczema: In addition to moisturizing, moderate-potency steroid creams or non-steroid creams may be needed, such as calcineurin inhibitors. These medications can control flare-ups and reduce recurrence.
3. Severe or widespread eczema: If local treatment is ineffective, the doctor will assess whether short-term use of oral antihistamines or immunomodulators is necessary, while combining wet compresses and other care methods to aid recovery.
In daily life, avoid scratching and excessive heat stimulation, choose cotton clothing, and use gentle cleansing products. If symptoms persist or worsen, please consult a doctor promptly to adjust the treatment plan. Long-term management combined with lifestyle improvements will better maintain skin stability.