Sleeping with someone who has urticaria (hives) usually doesn't transmit the disease, as urticaria itself is not contagious. However, for the comfort of both parties, it's advisable to pay attention to a few details.
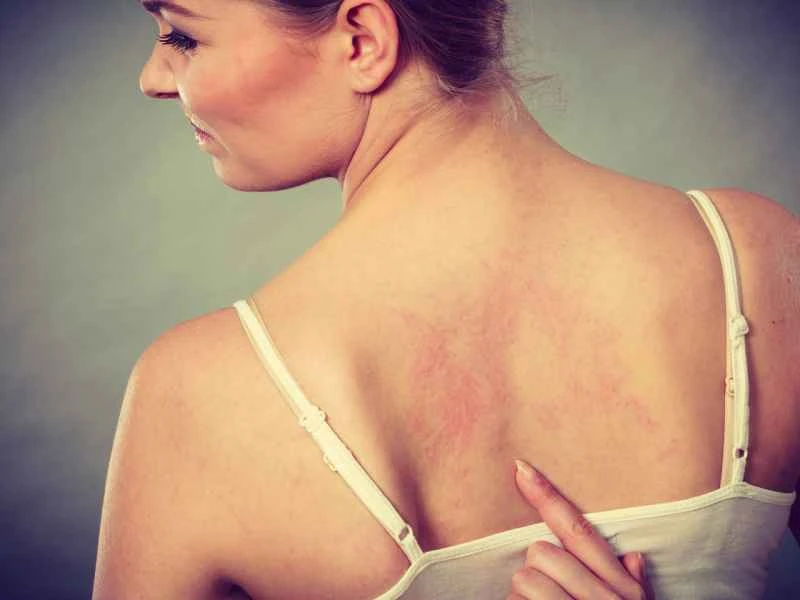

1. Urticaria is not transmitted through contact.
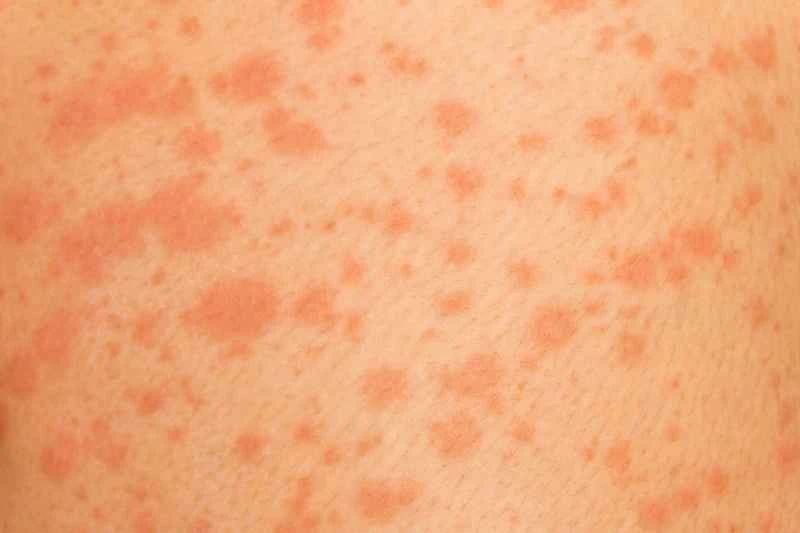
Urticaria is mostly caused by allergies, infections, or internal factors. It is an autoimmune reaction and will not be transmitted to others through everyday contact such as sleeping in the same bed or hugging.
2. Attention should be paid to potential discomfort factors.
In some patients, urticaria may be triggered by viral or bacterial infections. Although the rash itself is not contagious, the source of infection can spread through droplets. Additionally, nighttime itching may affect sleep quality, so a quiet environment is necessary.
3. Precautions when resting together
Keep the bed clean and change the sheets regularly; avoid using detergents that may cause allergies; if the patient experiences significant itching, it is advisable to have them wear loose cotton clothing to reduce skin friction.
In short, there's no need to worry excessively about infection when sleeping together. It's recommended to pay attention to the underlying cause of the infection; if symptoms such as fever or cough are present, seek medical attention promptly to rule out infection. Maintaining good ventilation and hygiene in daily life will not only comfort the patient but also allow both partners to rest more comfortably.


