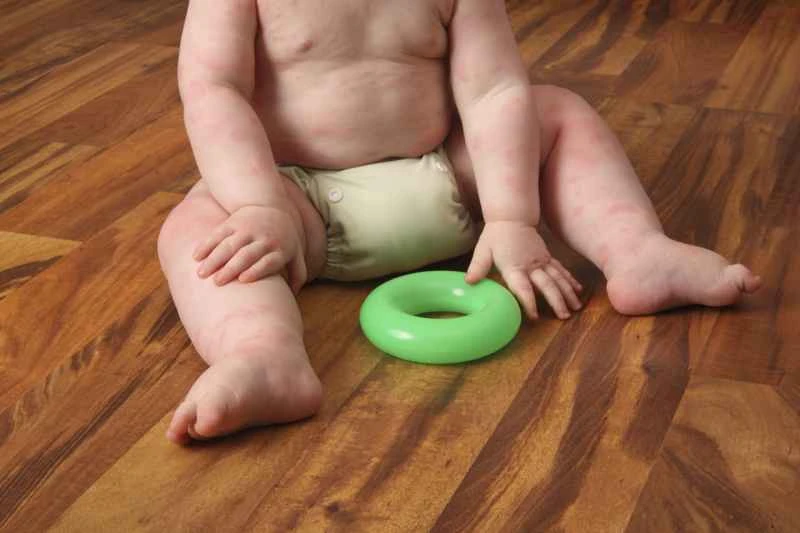
Urticaria can be relieved by controlling symptoms with medication and identifying triggers. It is recommended to seek medical attention promptly and receive standardized treatment under the guidance of a doctor.
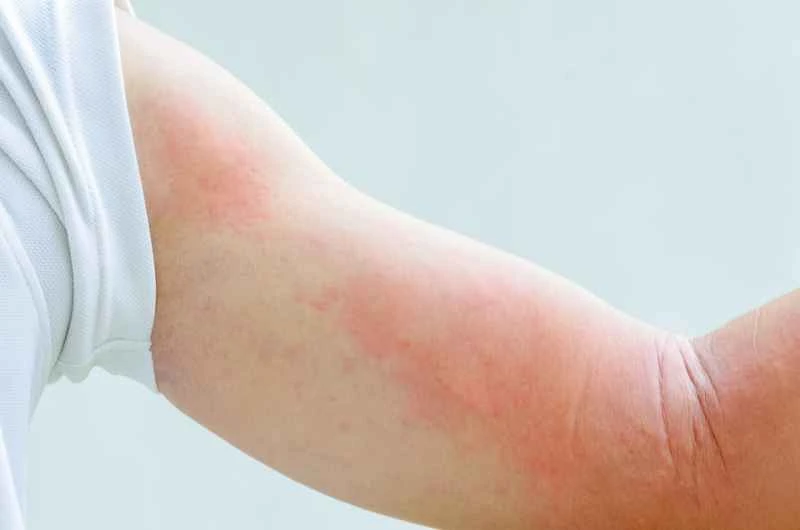
1. During an acute attack: Antihistamines are usually used to relieve itching and wheals. These medications can relieve discomfort quickly, but it is important to note that they may cause reactions such as drowsiness.
2. When recurring: It is necessary to record activities such as diet and contact with objects to help identify possible triggers, such as food, pollen or stress, and try to avoid them.
3. Daily care: Wear loose cotton clothing, avoid overheated baths, and keep your skin cool to help reduce irritation.
If symptoms persist or worsen, a follow-up visit to adjust the treatment plan is necessary. Regularly monitoring your own condition, reducing exposure to known triggers, and gradually improving lifestyle habits can all play a positive role in controlling urticaria.