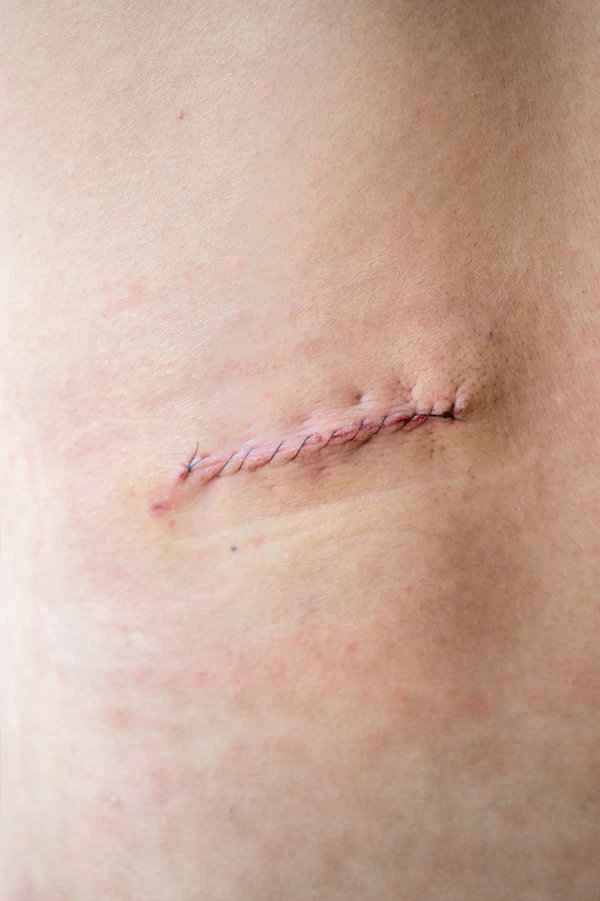
The process of scar removal involves a variety of methods aimed at reducing or eliminating scar tissue on the skin. Scar removal typically requires a comprehensive consideration of the scar's type, location, size, and the individual's health condition.
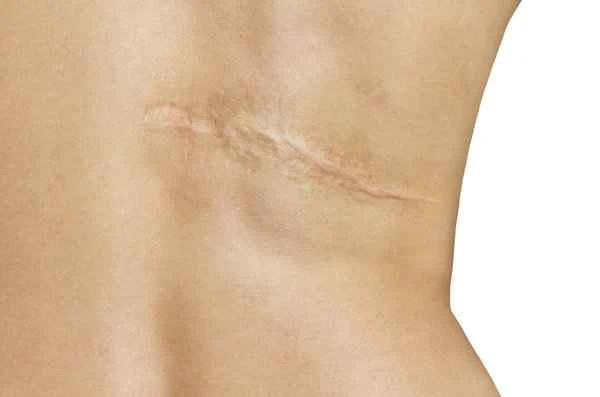
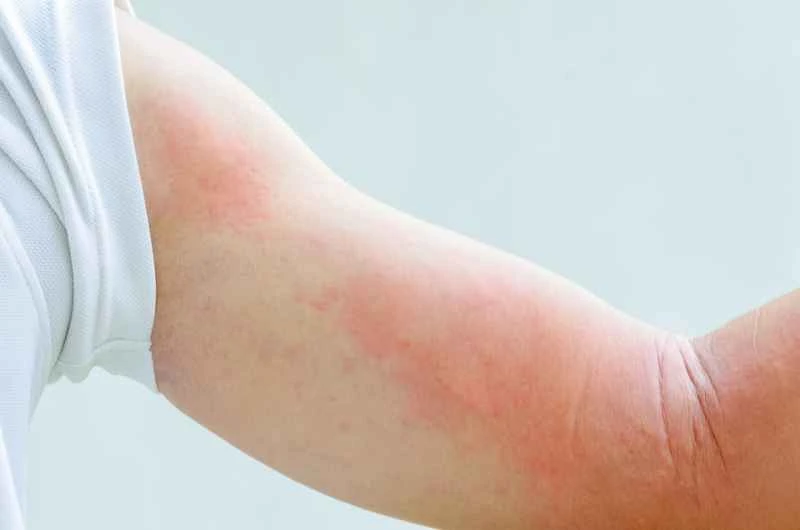
When treating scars, it's crucial to first identify the type of scar, as different types (such as hypertrophic scars, keloids, atrophic scars, etc.) may require different treatment methods. There are various methods for treating scars, including medication, laser therapy, surgical excision, silicone sheets, and pressure therapy. Medication may involve using ointments or gels containing ingredients such as vitamin E, silicone, and corticosteroids. These medications help reduce scarring by promoting normal skin cell growth and reducing inflammation. Laser therapy improves the appearance of scars by stimulating skin regeneration. Surgical excision is used for larger scars or those difficult to treat with other methods. It involves surgically removing the scar tissue and then repairing the wound with sutures or other methods. Silicone sheets and pressure therapy are also widely used for scar management. They reduce scar growth and promote softening and flattening by applying continuous pressure.
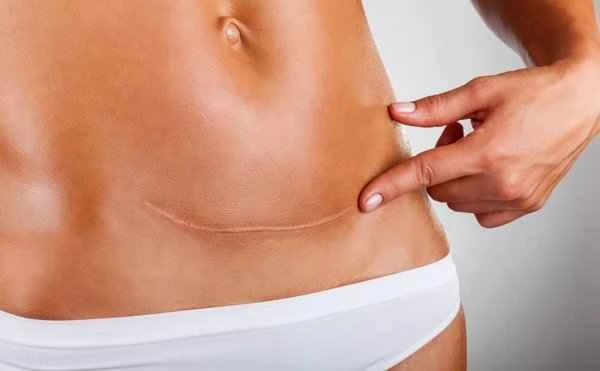
Patients may encounter some risks and misconceptions during scar treatment. Scar treatment is a long-term process that requires patience and perseverance. Some patients may overly rely on a single treatment method, neglecting the importance of comprehensive treatment. Finally, patients may experience side effects such as skin allergies and infections during scar treatment. Therefore, patients need to closely monitor changes in their skin and communicate with their doctor promptly during the treatment process.

[Management Tip:]
1. Choose the appropriate treatment method, selecting the most suitable treatment plan based on the type and size of the scar.
2. Pay attention to skin care during treatment to avoid infection and other complications.
3. Regular follow-up examinations should be conducted to assess the treatment effect and adjust the treatment plan if necessary.