Treatment for urticaria usually requires selecting appropriate medications based on specific symptoms and causes. There is no "best, fastest, and most effective" solution that works for everyone. It is recommended to use conventional medications such as antihistamines under the guidance of a doctor to control the condition.
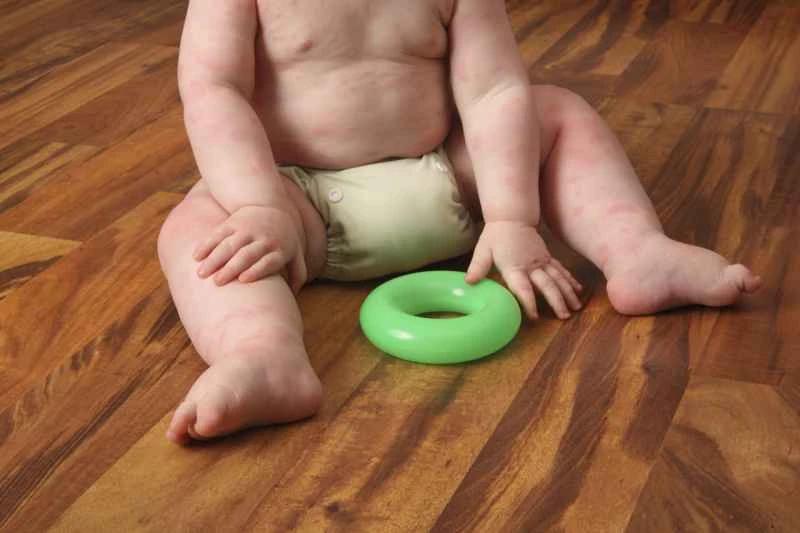

1. Commonly used oral medications: Most patients can use second-generation antihistamines, such as cetirizine or loratadine. These medications can help relieve itching and wheals, and have fewer side effects such as drowsiness.
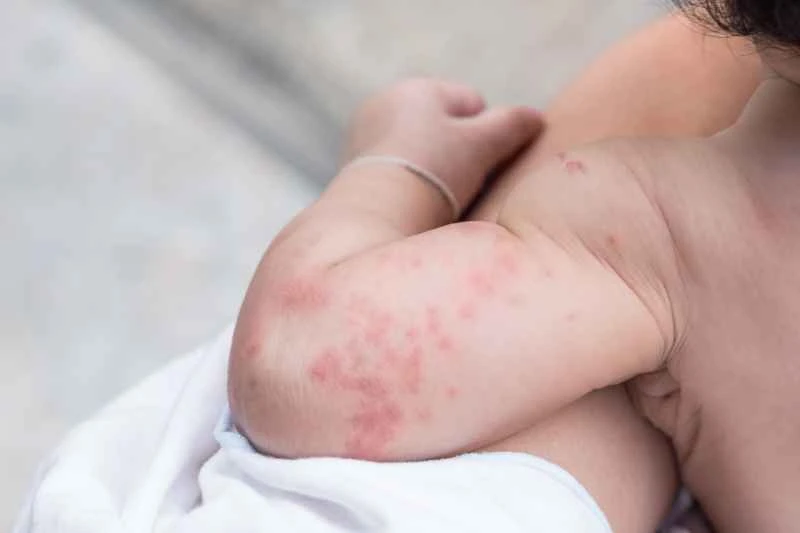
2. Management of severe symptoms: If the rash is extensive or recurs frequently, the doctor may adjust the dosage in the short term or consider combining it with other types of drugs, but it is necessary to strictly follow the doctor's instructions.
3. Local relief methods: Using topical antipruritic products such as calamine lotion can temporarily soothe skin discomfort and prevent scratching from causing infection.
In daily life, it's important to keep a record of factors that may trigger rashes, such as food and environmental changes, and consult a dermatologist promptly. Keeping your skin clean and wearing loose clothing can also help reduce irritation. If you experience severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing, seek immediate medical attention.


