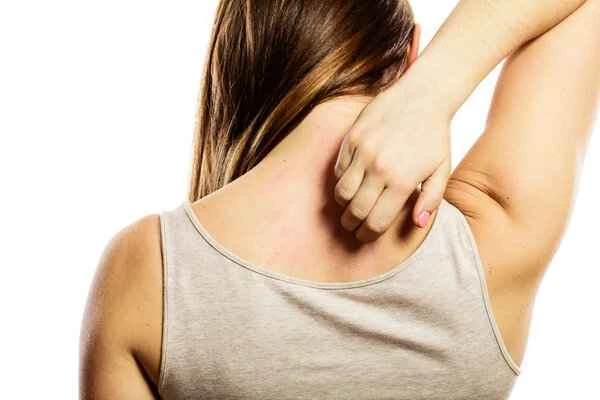
The duration of medication for urticaria varies from person to person, typically ranging from several weeks to several months, depending on the type of urticaria and individual constitution. It is recommended to use medication regularly under the guidance of a doctor and to combine this with daily care to promote recovery.
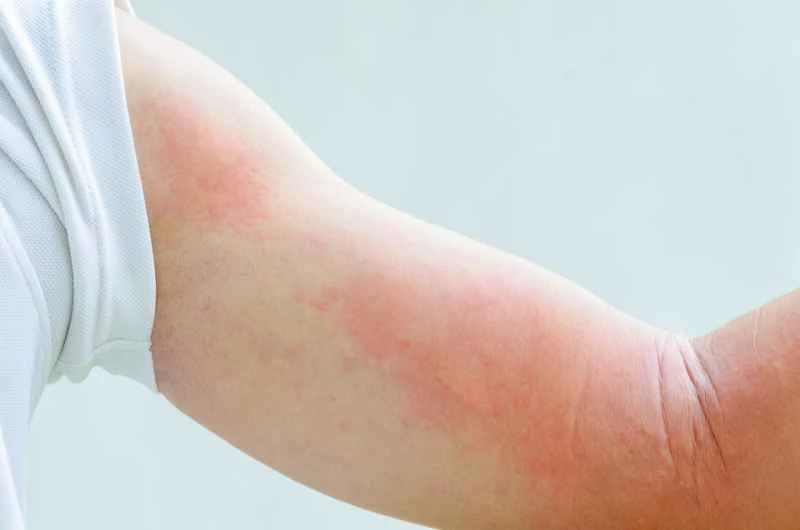
1. Acute urticaria: If caused by a clear cause such as food or infection, symptoms may subside within days to weeks after avoiding the trigger and taking medication, but the course of treatment recommended by the doctor must be completed.

2. Chronic urticaria: The course of the disease often exceeds 6 weeks, and the treatment time may be long. Doctors often develop a phased treatment plan to control symptoms and reduce recurrence through medication. Some patients need to continue medication for several months or even longer.
3. Individual differences: Factors such as response to medication, lifestyle habits, and immune status can all affect the recovery progress, so the duration of medication may vary greatly from person to person.
In general, never stop taking medication or adjust the dosage on your own. Even if symptoms temporarily disappear, you should still have regular follow-up appointments so your doctor can assess any changes in your condition. Also, keep a record of factors that may trigger the rash, such as diet and stress, and try to avoid them in your daily life. This will help shorten the treatment course and stabilize recovery.