Treatment for papular urticaria typically involves the use of specific topical medications to relieve symptoms. Papular urticaria is a common allergic skin reaction, usually manifesting as red, swollen papules or plaques accompanied by intense itching. The key to treating papular urticaria is relieving symptoms, reducing inflammation, and avoiding allergens. The choice of topical medication is usually based on the severity of the patient's symptoms and individual constitution. Commonly used topical medications include ointments containing corticosteroids, which are effective in reducing inflammation and itching. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and antihistamines are also widely used to relieve the symptoms of papular urticaria. These medications work by suppressing the inflammatory response and reducing histamine release.

Choosing the right topical medication is crucial for treating papular urticaria. Corticosteroid creams relieve symptoms by suppressing the inflammatory response, while nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) creams alleviate symptoms by inhibiting the production of inflammatory mediators. Antihistamines reduce itching by blocking the action of histamine. These medications have different mechanisms of action, but they all work together to reduce inflammation and itching, thereby alleviating the symptoms of papular urticaria. Choosing the right medication and using it as prescribed by a doctor can effectively control the symptoms of papular urticaria and prevent the condition from worsening.
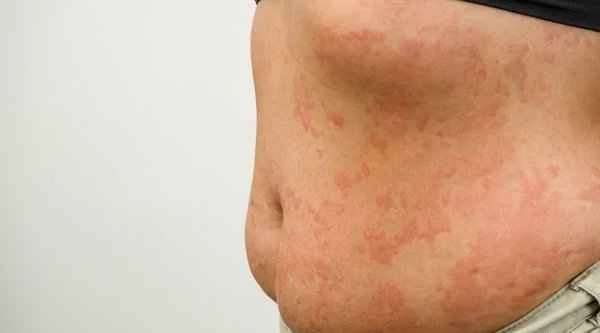
Patients may encounter some misconceptions when treating papular urticaria. For example, some patients may over-rely on medication, neglecting the importance of identifying and avoiding allergens. Some patients may mistakenly believe that all topical medications are suitable for all types of papular urticaria, which may lead to the use of inappropriate medications and ineffective symptom relief. When using topical medications to treat papular urticaria, patients should choose appropriate medications under the guidance of a doctor and pay attention to avoiding possible allergens to achieve the best treatment results.
[Management Tip:]
1. Use a doctor-recommended topical medication, such as a corticosteroid cream, to relieve symptoms.
2. Take precautions to avoid potential allergens, such as certain foods, insect bites, or contact allergens.
3. If symptoms worsen or persist, seek medical attention promptly for further treatment advice.