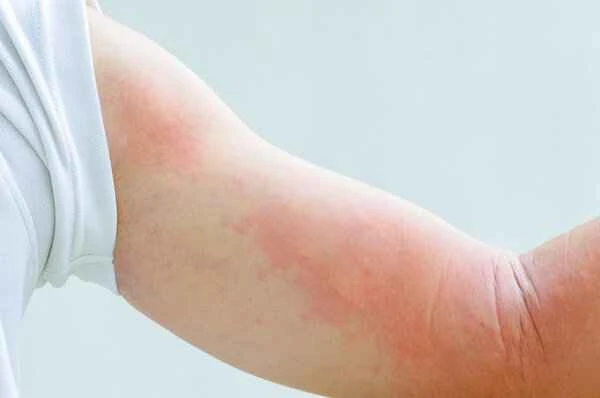
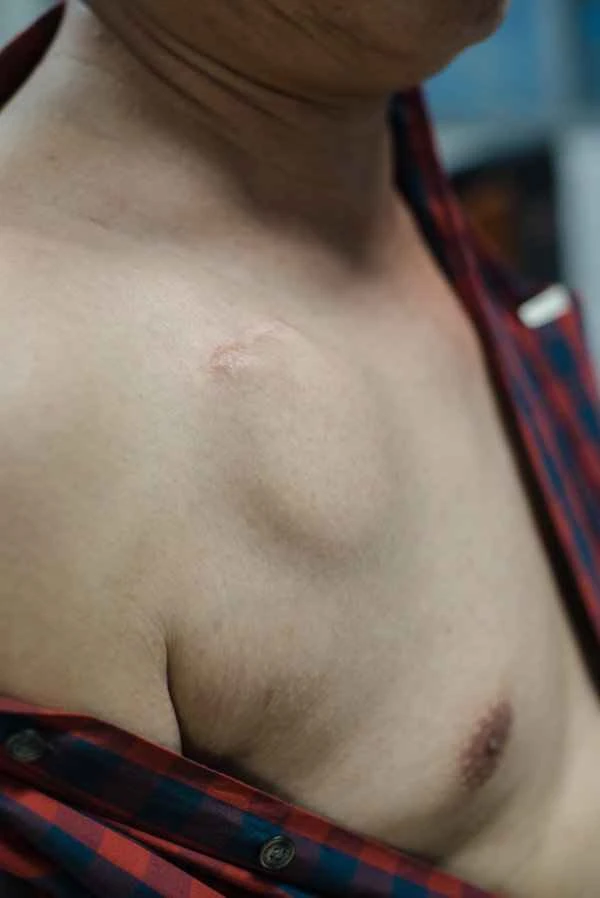
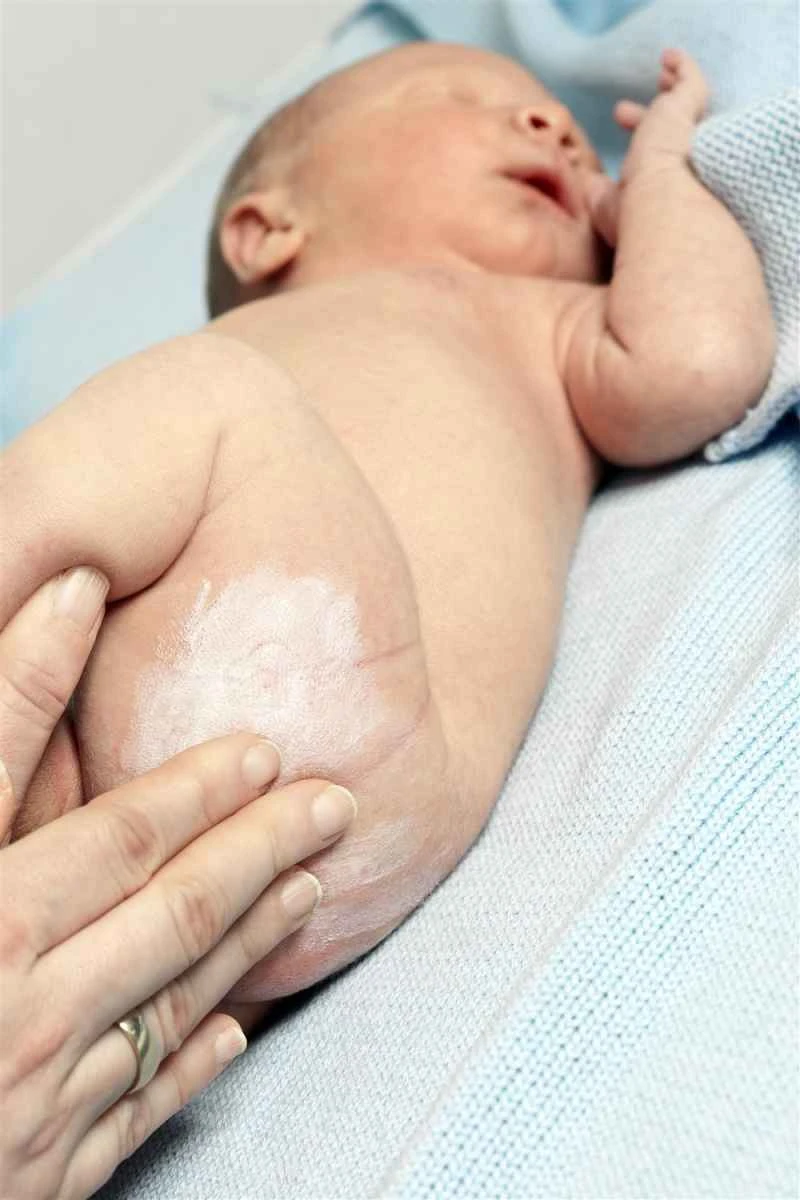
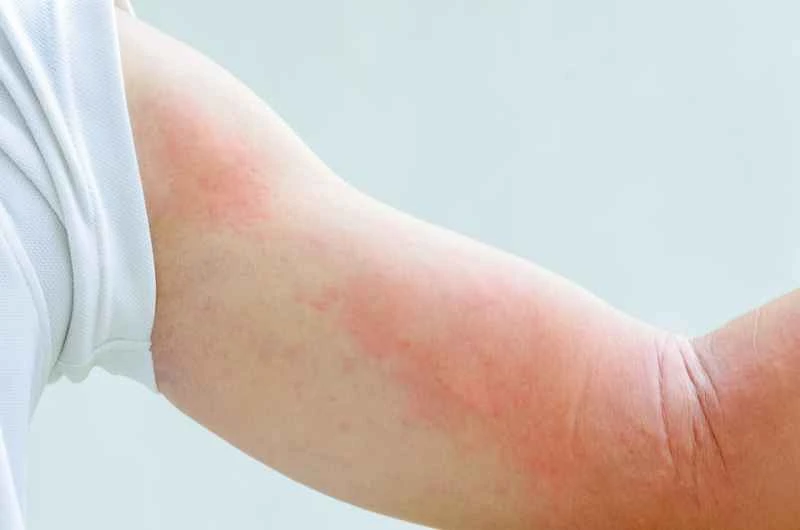
Urticaria usually resolves on its own and is generally not contagious. It is recommended to seek medical attention promptly if symptoms appear to determine the cause and avoid delaying treatment by self-medicating.
The specific explanation is as follows:
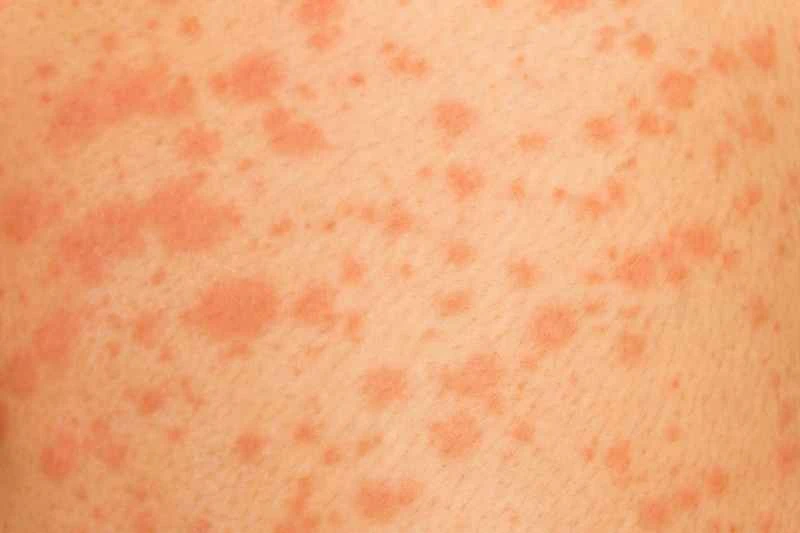
1. Regarding the resolution of symptoms: Most cases of urticaria will resolve on their own within hours to days, but they may recur. If the symptoms persist for more than 6 weeks, it is recommended to consult a doctor to investigate chronic causes.
2. Regarding infectivity: Urticaria is an immune system-related reaction and is not directly caused by bacteria or viruses. Therefore, it cannot be transmitted to others through contact, droplets, or other means.
3. Common triggers: Food, medication, temperature changes, stress, etc. can all trigger it, but the specific cause varies from person to person and needs to be analyzed in combination with individual circumstances.
Daily advice includes recording changes in diet and environment before an attack to help doctors identify the trigger; during an attack, avoid scratching the skin and use cold compresses to relieve itching; if accompanied by shortness of breath, swelling of the eyelids and lips, seek medical attention immediately.