Urticaria can be managed to reduce recurrence through standardized treatment and long-term management, but individual differences should be considered. It is recommended to undergo comprehensive treatment under the guidance of a doctor.
1. Identify the trigger: Common causes include food, pollen, medication, or stress. Recording the environment and diet during an attack can help identify the trigger.
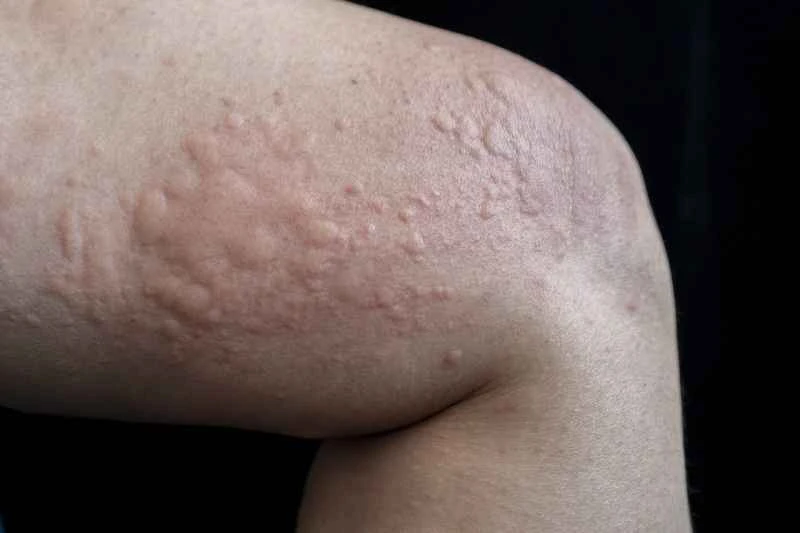
2. Use medication correctly: Doctors often prescribe anti-allergy medications to control itching and hives. These medications should be used according to the prescribed course of treatment. Avoid stopping the medication or adjusting the dosage on your own.
3. Daily protection: Wear loose cotton clothing and avoid overheated environments; bath water temperature should not be too high to reduce skin irritation.
4. Lifestyle adjustments: Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and moderate exercise can help regulate immunity; relaxation activities can help relieve emotional stress.
Regular follow-up visits are recommended to assess changes in the condition. If recurrences are frequent, allergen testing may be considered. Pay close attention to your own reactions and communicate with your doctor promptly to adjust the treatment plan. Most patients can achieve good control through continuous management.