Treatment for fungal infections of the soles of the feet primarily involves controlling and eliminating the fungus through medication and daily care. The core of treatment lies in the use of antifungal medications, which can be applied topically or taken orally to the infected area. These medications destroy the cell walls of the fungus or inhibit its growth, thereby achieving a cure. In addition to medication, keeping the feet clean and dry is also an important part of treatment, as fungi thrive in moist environments.
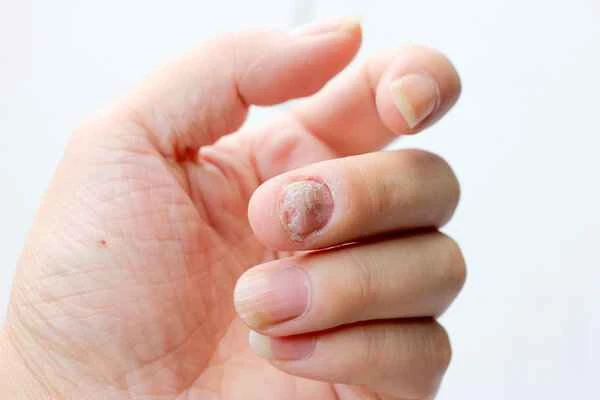
In treating fungal infections of the soles of the feet, the choice of medication and its application method are crucial. Topical antifungal medications act directly on the infected site, reducing the number of fungi and relieving symptoms. Oral antifungal medications act systemically and are more suitable for cases where topical treatment is ineffective or the infection is widespread. These medications work through different mechanisms of action against fungi, such as disrupting fungal cell walls and interfering with fungal metabolism, thereby inhibiting or eliminating the fungus. Simultaneously, patients need to pay attention to daily care, such as keeping feet dry, wearing breathable shoes and socks, and avoiding barefoot walking, to reduce the growth environment for fungi and improve treatment effectiveness.
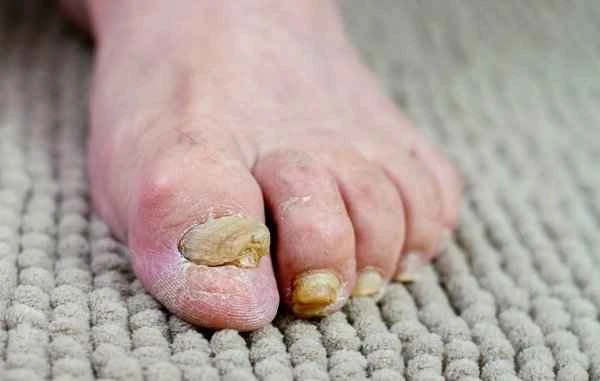
When treating fungal infections of the soles of the feet, patients may encounter some common misconceptions, such as believing that symptom relief means the infection has been completely eliminated, or that using over-the-counter ointments can completely cure the infection. These misconceptions can lead to incomplete treatment or recurrent infections. During treatment, patients should strictly follow their doctor's instructions regarding medication use and have regular follow-up examinations to ensure the infection is effectively controlled. Side effects such as skin irritation and allergic reactions may occur during treatment; therefore, it is important to closely monitor the body's reactions while using medication and communicate with the doctor promptly.
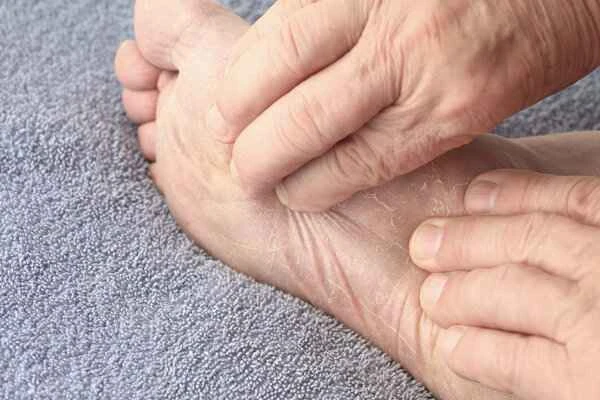
[Management Tip:]
1. Follow your doctor's instructions and continue using antifungal medication until the course of treatment is completed.
2. Keep your feet clean and dry, and avoid soaking your feet for a long time or walking barefoot.
3. Regular follow-up examinations should be conducted to monitor the infection status and adjust the treatment plan in a timely manner.
4. If redness, swelling, or increased pain occurs, seek medical attention promptly.


