Keloids are an over-repairing skin reaction that forms on the vermilion border of the lips. Removing them requires a combination of treatment methods. Keloids form because the skin produces excessive collagen during the healing process, leading to local tissue hyperplasia and the formation of a hard lump. Removing keloids on the vermilion border typically involves a combination of medication, physical therapy, and surgery.
Drug therapy is the foundation of keloid treatment. Topical corticosteroids can inhibit excessive collagen synthesis, thereby reducing the size and hardness of keloids. Drugs such as 5-fluorouracil can also be used to inhibit keloid growth. The mechanism of action of these drugs is mainly through inhibiting cell proliferation and reducing inflammatory responses, thus achieving the goal of treating keloids. Simultaneously, oral medications such as vitamin E and silicone gel can also provide adjunctive treatment, helping to soften scar tissue and promote its recovery.
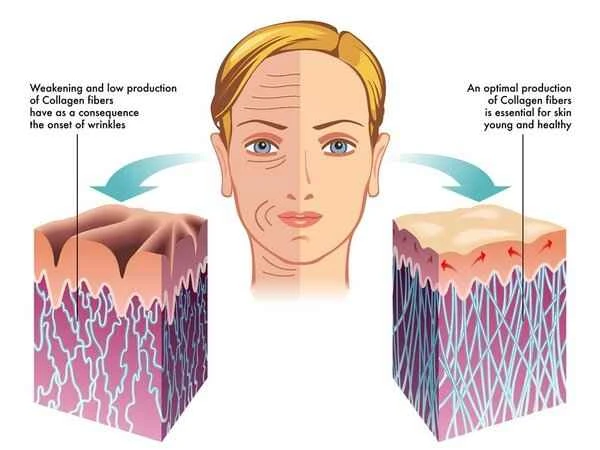
Physical therapy is also an important method for treating keloids. Laser therapy, cryotherapy, and radiation therapy are all methods used to treat keloids. Laser therapy uses specific wavelengths of laser light to irradiate the keloid, promoting the breakdown of scar tissue and reducing the hardness and size of the scar. Cryotherapy uses low temperatures to freeze the keloid, causing it to die and slough off, thus achieving the therapeutic goal. Radiation therapy uses radiation to irradiate the keloid, inhibiting its growth and reducing its hardness and size. The mechanism of these physical therapies is mainly through destroying scar tissue, promoting its breakdown and absorption, thereby achieving the goal of treating keloids.
Finally, surgery is the ultimate treatment for keloids. Surgical excision of the keloid can completely remove scar tissue, but surgery also carries certain risks, such as infection, bleeding, and recurrence. When choosing surgical treatment, factors such as the patient's condition, the size and location of the keloid need to be considered to determine the best treatment plan.
It's important to note that keloid treatment is a long-term process that requires patience and confidence from the patient. Side effects may occur during treatment, such as local redness, swelling, and pain; these usually disappear gradually after treatment. However, it's crucial to be aware of potential complications such as infection and bleeding. These complications could lead to treatment failure, therefore close monitoring of the patient's condition and timely adjustments to the treatment plan are essential.
[Management Tip:]
1. Topical application of corticosteroid medications can inhibit the growth of keloids.
2. Regular laser or cryotherapy treatments can promote the breakdown and absorption of scar tissue.
3. When surgically removing keloids, it is necessary to take precautions to prevent complications such as infection and bleeding.
4. During treatment, it is necessary to closely monitor changes in the patient's condition and adjust the treatment plan in a timely manner.