Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp is a common skin condition characterized by erythema, scaling, and excessive sebum production on the scalp. The key to improving seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp lies in controlling sebum production, reducing inflammation, and eliminating pathogenic microorganisms.
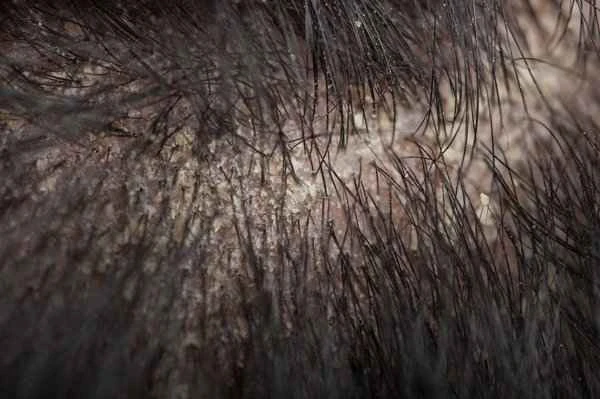
Strategies for improving seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp mainly include using antifungal medications, controlling sebum secretion, and reducing inflammation. Antifungal medications such as ketoconazole can effectively inhibit the growth of Malassezia and reduce inflammation. Using shampoos containing tar, sulfur, or salicylic acid can help remove dandruff from the scalp and reduce sebum secretion. These methods work synergistically to improve the symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis. During treatment, dietary control is also necessary, avoiding excessive intake of sugar and fat to reduce sebum secretion and thus alleviate inflammation.

When treating seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp, it's important to be aware of some potential risks and common misconceptions. Overuse of steroid-containing ointments may lead to thinning of the skin and pigmentation problems. Treating seborrheic dermatitis is a long-term process requiring patience and consistent treatment; a complete cure cannot be expected in a short period. Finally, the causes of seborrheic dermatitis are complex, potentially related to genetics, environment, diet, and other factors. Therefore, treatment should consider all these factors comprehensively, rather than relying solely on medication.
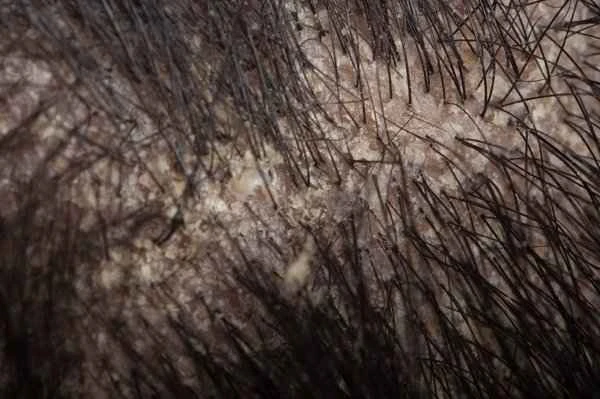
[Management Tip:]
1. Use antifungal shampoos, such as those containing ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or coal tar.
2. Keep your scalp clean and avoid overuse of products such as conditioner and hairspray.
3. Pay attention to a healthy diet, reduce your intake of sugar and fat, and eat more foods rich in vitamins.
4. Regularly monitor your scalp condition. If it worsens or does not improve, seek medical attention promptly.


