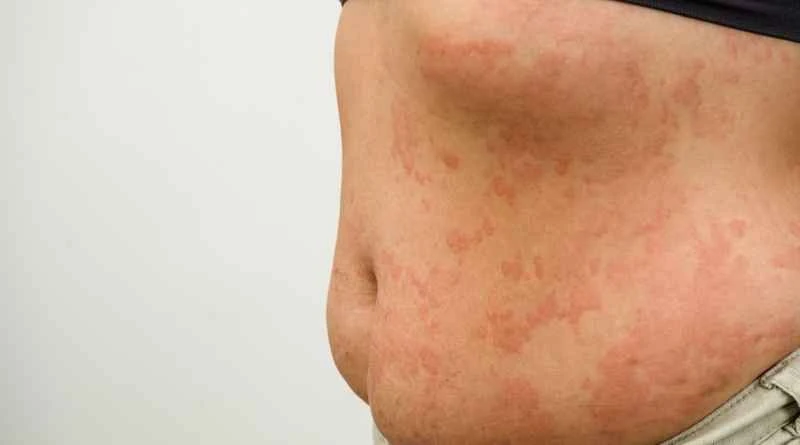
Postherpetic neuralgia, also known as shingles neuralgia, refers to the severe pain that patients experience even after the herpes zoster lesions on the skin have healed. Treatment for shingles neuralgia mainly relies on the combined use of antiviral drugs, analgesics, and neuroprotective agents to reduce pain, shorten the course of the disease, and prevent the occurrence of sequelae.
Treatment for neuralgia caused by shingles begins with antiviral drugs, such as acyclovir, to inhibit viral replication and reduce viral damage to nerves. To relieve pain, doctors may prescribe analgesics such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antidepressants, or anticonvulsants. These medications regulate the function of the nervous system, thereby reducing pain. Neuroprotective agents, such as B vitamins, can promote nerve repair and accelerate the recovery process. These medications work together to form a comprehensive treatment system, addressing the issue from different angles to achieve the best therapeutic effect.
When treating neuralgia caused by shingles, it's important to note that while medication is the primary treatment method, the patient's psychological state also significantly impacts treatment effectiveness. Prolonged pain can lead to anxiety, depression, and other psychological problems, which in turn can affect pain perception and treatment outcomes. Therefore, in addition to medication, attention should be paid to the patient's mental health during treatment. If necessary, seeking help from a mental health professional for psychological intervention can improve the overall treatment outcome.
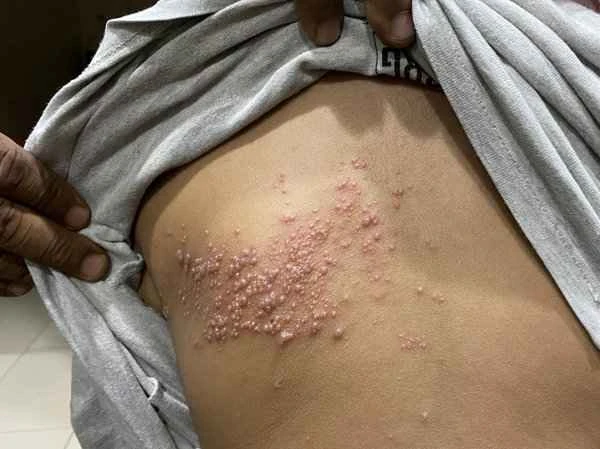
[Management Tip:]
1. Seek medical attention promptly, follow the doctor's treatment plan, and take medication on time.
2. Maintain good lifestyle habits, such as regular sleep and a balanced diet.
3. Pay attention to psychological adjustment and seek psychological counseling help when necessary.