Completely curing urticaria requires patient cooperation with treatment and long-term management of triggering factors. It is recommended to seek medical attention promptly and take comprehensive measures under the guidance of a doctor.
1. Use medication correctly to control symptoms.
Doctors often prescribe anti-allergy medications to relieve itching and hives. These medications must be used according to the prescribed course of treatment. Even if symptoms improve, medication should not be stopped on your own to prevent recurrence.
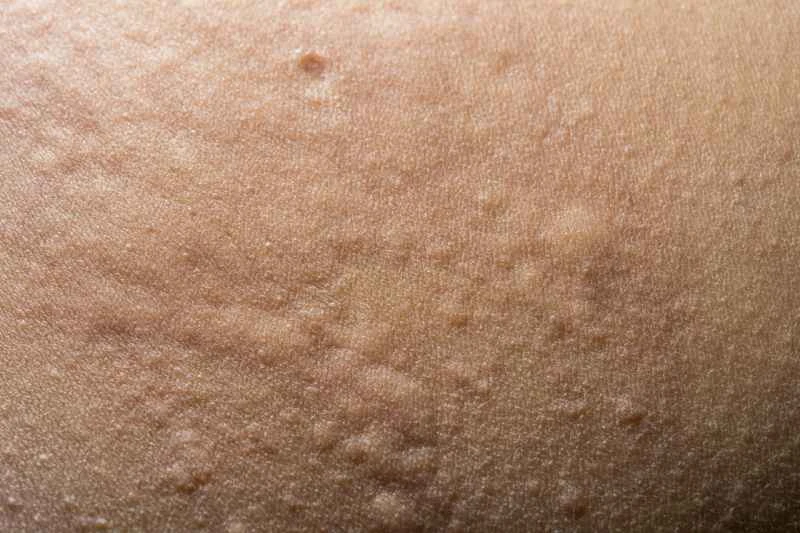
2. Actively seek out and avoid triggers.
Common triggers include food, pollen, dust mites, stress, or temperature changes. Try keeping a record of your daily diet and environment to help identify possible causes and take precautions to avoid them in your daily life.
3. Adhere to daily skin care routine
Avoid scratching your skin, and avoid using excessively hot water when bathing. Wear loose-fitting cotton clothing. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and engaging in moderate exercise can help reduce the frequency of flare-ups.
4. Regular follow-up visits to adjust the treatment plan.
The course of urticaria varies from person to person and may last for a long time in some cases. Regularly communicating with your doctor about your recovery progress allows for adjustments to the treatment plan as needed.
If symptoms recur, do not try folk remedies. Maintain regular communication with a dermatologist; through scientific treatment and lifestyle management, most people can effectively control their symptoms.


