Urticaria itself is usually not life-threatening, but in rare severe cases it may pose risks. It is recommended to seek medical attention promptly and follow your doctor's instructions. The following is a detailed explanation:
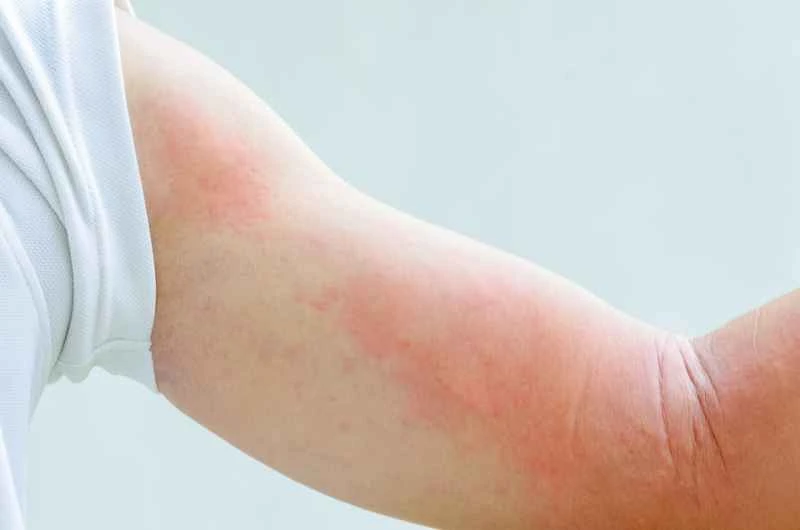
1. Security under normal circumstances
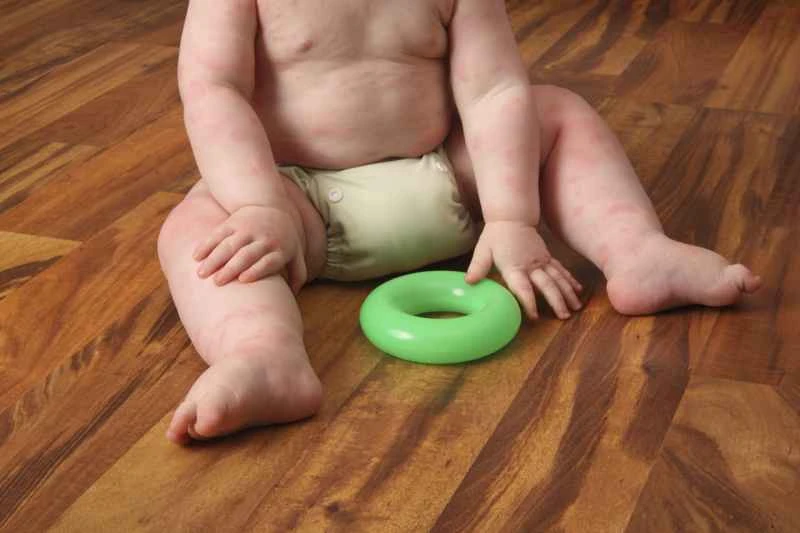

Most cases of urticaria present as itchy, red, and swollen wheals that are short-lived and can be relieved with medication or lifestyle adjustments. They do not affect normal lifespan.
2. Serious reactions to be wary of
If accompanied by symptoms such as difficulty breathing, tightness in the throat, or dizziness, it may develop into anaphylactic shock. Such emergencies require immediate medical attention, otherwise they may be life-threatening.
3. The impact of long-term chronic urticaria
Some patients have a long course of illness, and repeated relapses may affect their sleep and mood, but with proper treatment, symptoms can usually be controlled and their quality of life can be maintained.
Daily advice: Avoid known allergens, such as food and pollen; record the pattern of flare-ups for easier diagnosis by your doctor; use antihistamines as prescribed during acute flare-ups, and never stop taking medication on your own. Maintain a positive attitude; most patients can live peacefully with urticaria.


