When treating urticaria, antihistamines can usually be used under the guidance of a doctor to quickly relieve symptoms, but the specific medication should be chosen based on the cause and symptoms. The following are common medication guidelines:
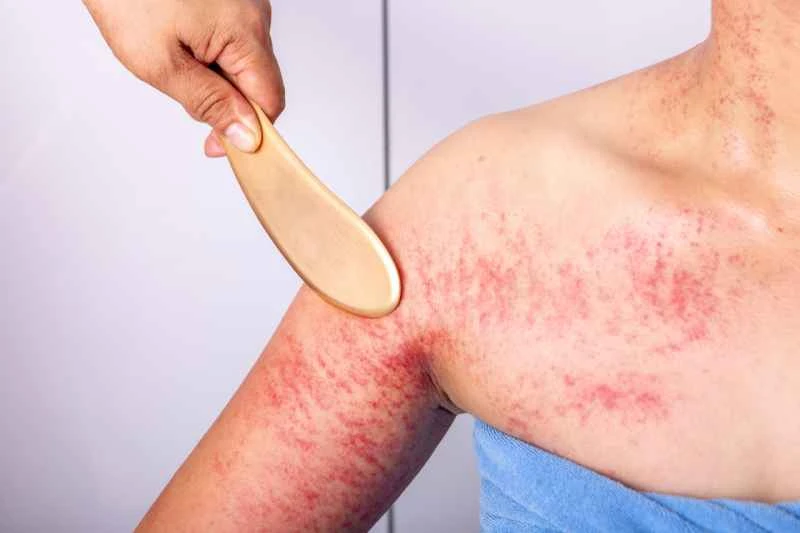
1. Mild acute onset: If the rash is small and the itching is not severe, second-generation antihistamines such as loratadine and cetirizine can be used. These drugs are usually taken once a day and have fewer side effects such as drowsiness.
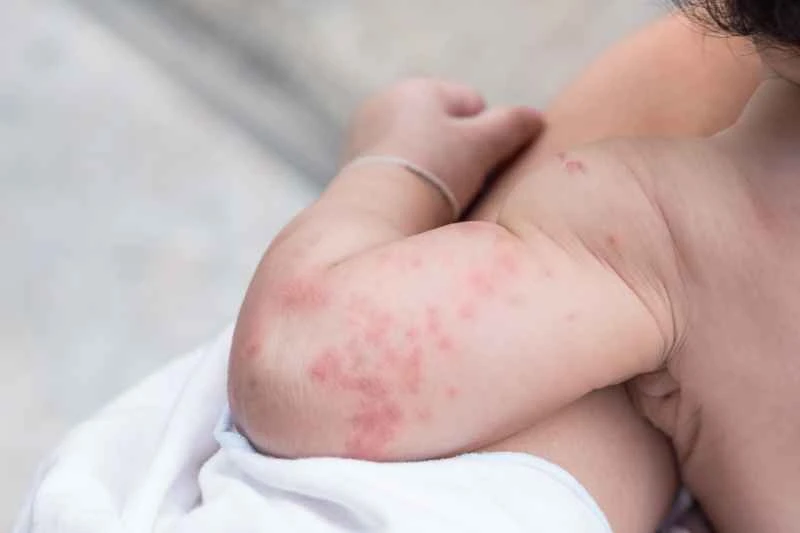
2. Recurring or severe symptoms: If wheals recur or are accompanied by significant swelling, doctors may recommend the combined use of different antihistamines or the short-term addition of other types of medications to help control the condition.
3. Medication use in special populations: Children, pregnant women or breastfeeding patients need to strictly follow the doctor's instructions for medication adjustment, such as choosing a dosage form that is safe for children or avoiding the use of drugs that may affect the fetus.
In addition to medication, recording factors such as diet and environment during an attack can help identify triggers. If symptoms do not improve after medication, or if severe conditions such as shortness of breath occur, please seek medical attention immediately. In daily life, avoid scratching your skin, and wearing loose clothing can also reduce discomfort.