Treatment for urticaria usually requires choosing medication based on the specific situation. It is recommended to use antihistamines under the guidance of a doctor and combine them with daily care to improve symptoms.
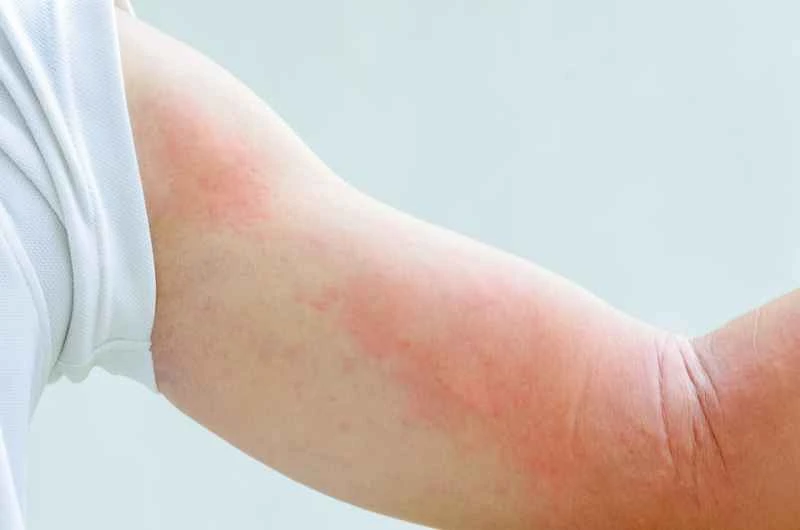
1. Commonly used oral medications: Most patients can use second-generation antihistamines, such as cetirizine or loratadine. These medications can help relieve itching and wheals, and have relatively few side effects such as drowsiness. If the effect is not obvious, the doctor may adjust the dosage or combine other medications.
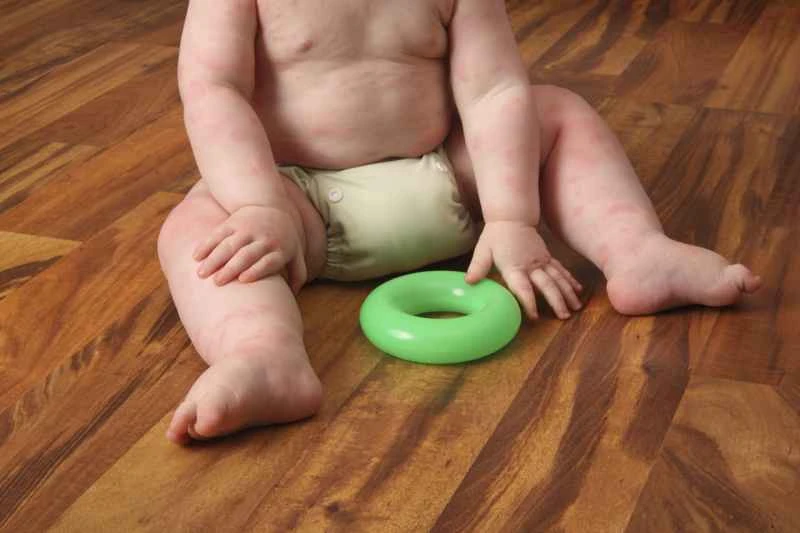

2. Special Case Management: For cases with severe or recurrent symptoms, doctors may prescribe other types of medications, such as hormonal drugs, for a short period of time. However, it is essential to strictly follow the doctor's instructions and avoid long-term self-medication.
3. Topical medications as an adjunct: Topical antipruritic agents such as calamine lotion can temporarily relieve skin discomfort, but oral medications are still the main way to control the condition.
In your daily life, be mindful of factors that may trigger urticaria, such as food, stress, or environmental changes, and avoid scratching your skin. If symptoms persist or worsen after using medication, please consult your doctor promptly. They will adjust the treatment plan based on your response to help you better manage your condition.