Urticaria can be effectively controlled through systemic treatment and long-term management, but a complete cure requires patience. It is recommended to address the issue from three aspects: identifying the triggers, using medication correctly, and adjusting lifestyle habits.

1. Identify and avoid triggers.

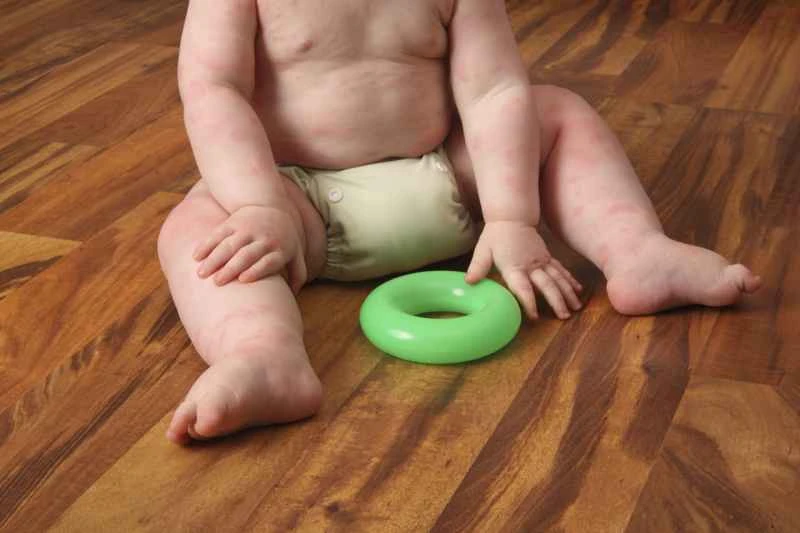
Some cases of urticaria are related to food, pollen, dust mites, or stress. Keeping a record of dietary and environmental changes before and after an attack can help identify possible causes and avoid them as much as possible.
2. Follow the doctor's instructions for standardized treatment.
Doctors often prescribe anti-allergy medication to control symptoms. Please use it according to the prescribed course of treatment and do not stop taking the medication on your own. If symptoms recur frequently, consult your doctor to see if further examination is needed.
3. Maintain stable lifestyle habits
Maintain a regular sleep schedule, wear loose-fitting cotton clothing, and avoid bathing in excessively hot water. Appropriate exercise and relaxation can also help reduce the frequency of attacks.
Pay attention to your body's reactions in daily life. If symptoms suddenly worsen or are accompanied by difficulty breathing, seek medical attention promptly. With consistent management and patient adjustments, most people can achieve long-term symptom relief.