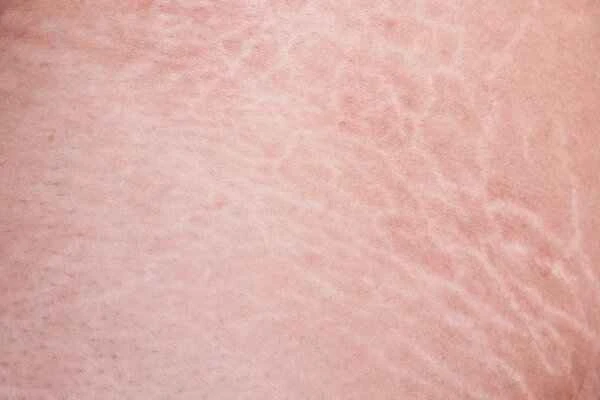
Treatment for urticaria usually requires selecting appropriate medications based on specific symptoms and causes. It is recommended to use antihistamines and other medications under the guidance of a doctor to control the condition.
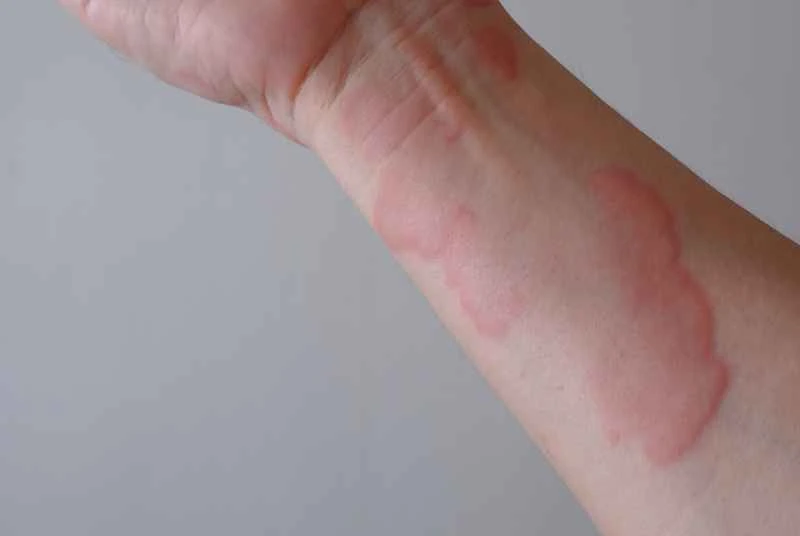
1. Commonly used oral medications: Most patients relieve itching and hives by taking oral antihistamines (such as loratadine and cetirizine). These medications can help reduce allergic reactions, but it is important to note that they may cause side effects such as drowsiness.
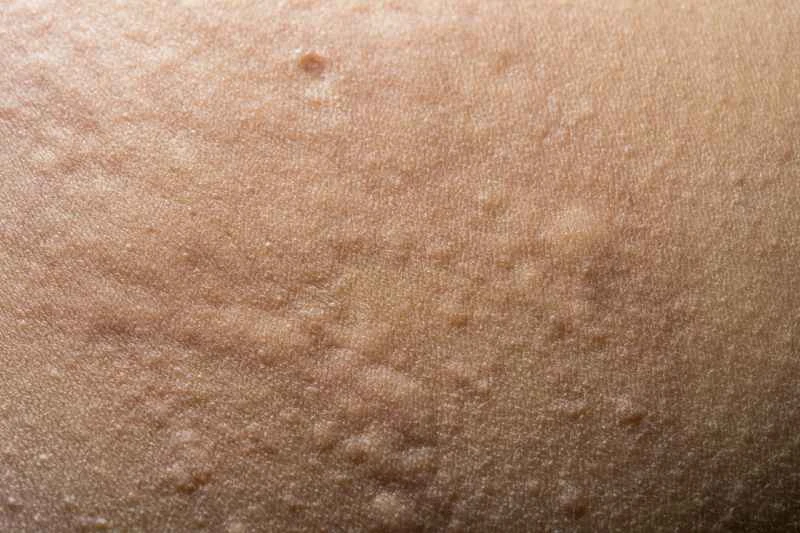
2. Management of severe cases: If the symptoms are severe or recurrent, doctors may prescribe hormone medications for a short period of time to quickly control the inflammation, but it is not advisable to use them on your own for a long period of time.
3. Adjunctive treatment methods: For chronic urticaria, it is sometimes necessary to combine other medications (such as anti-inflammatory drugs) or identify allergens, and reduce the frequency of attacks through lifestyle modifications.
In daily life, pay attention to recording your diet and environmental factors during flare-ups, avoid scratching your skin, and wear loose clothing. If medication is ineffective or symptoms worsen, please seek medical attention promptly for a follow-up examination so that the treatment plan can be adjusted.