Urticaria is usually triggered by factors such as allergies, infections, or physical irritants. While it may be difficult to completely cure in some patients, symptoms can be effectively controlled through proper treatment and daily management. It is recommended to use antihistamines under the guidance of a doctor and to carefully identify the triggering factors.
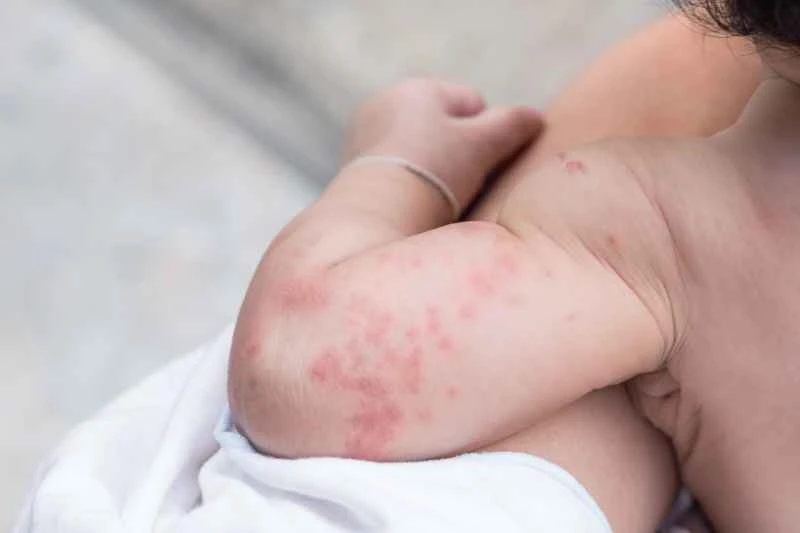
1. Common triggering factors

Food allergies (such as seafood and nuts), drug reactions, and environmental factors such as pollen or dust mites can all trigger localized redness and itching of the skin. In addition, emotional stress, temperature changes, or physical stimuli such as friction can also cause symptoms.
2. Treatment and Drug Selection
Oral antihistamines (such as loratadine) are commonly used to relieve itching and wheals. If symptoms recur, your doctor may adjust the medication regimen. Please avoid long-term self-medication and use medication only as directed by your doctor.
3. The Importance of Daily Management
Recording your diet, environment, and other activities during an attack can help identify individual triggers. Wearing loose cotton clothing, avoiding overheated environments, and maintaining a calm state of mind can reduce the frequency of attacks.
It is recommended to consult a dermatologist regularly and gradually establish a management approach suitable for your individual needs, combining medication with lifestyle adjustments. Through continuous observation and scientific management, most people can achieve long-term symptom relief.


