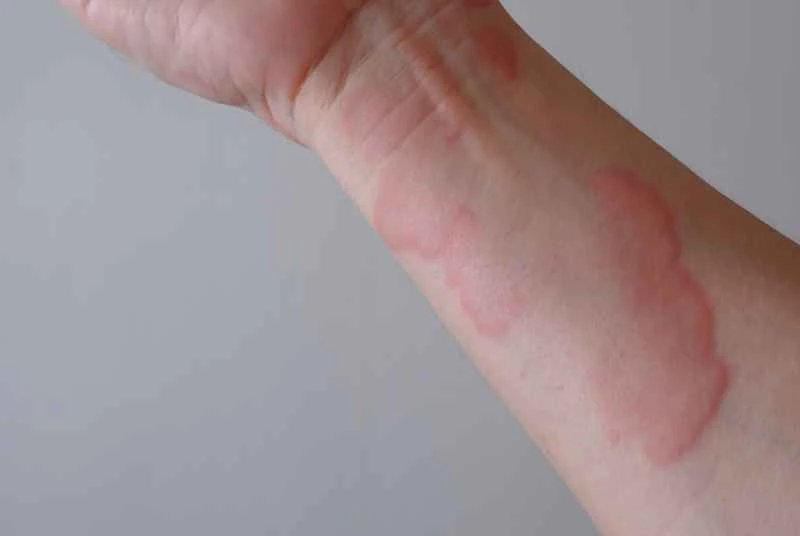
Dermatographic urticaria can be managed with comprehensive treatment to alleviate symptoms and reduce recurrence, but complete eradication is not easy and requires long-term adherence to care and treatment. It is recommended to use medication under the guidance of a doctor and combine this with adjustments to daily habits.
Specifically, we can start from the following aspects:

1. **Proper Medication Use:** Doctors often prescribe anti-allergy medications to relieve itching and hives. These medications must be taken according to the prescribed course of treatment. Do not stop taking the medication or change medications on your own.
2. **Skin protection:** Avoid scratching or rubbing your skin. Wear loose, soft cotton clothing. When bathing, the water temperature should not be too high to reduce skin irritation.
3. **Find the triggers:** Observe whether the attack is more likely to occur after stress, fatigue, or contact with certain materials. Try to record and avoid possible triggers.
4. **Strengthen physical fitness:** Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and moderate exercise can help improve the immune system, but strenuous exercise that causes sweating should be avoided.
Patients should patiently cooperate with treatment and avoid rushing for quick results. If symptoms persist or worsen, seek timely follow-up examination and communicate with the doctor to adjust the treatment plan. Scientific management can improve quality of life and stabilize the condition.


