Urticaria is not contagious from person to person, so parents can rest assured. It is a skin allergic reaction, and children with this condition need prompt medical attention and careful daily care.
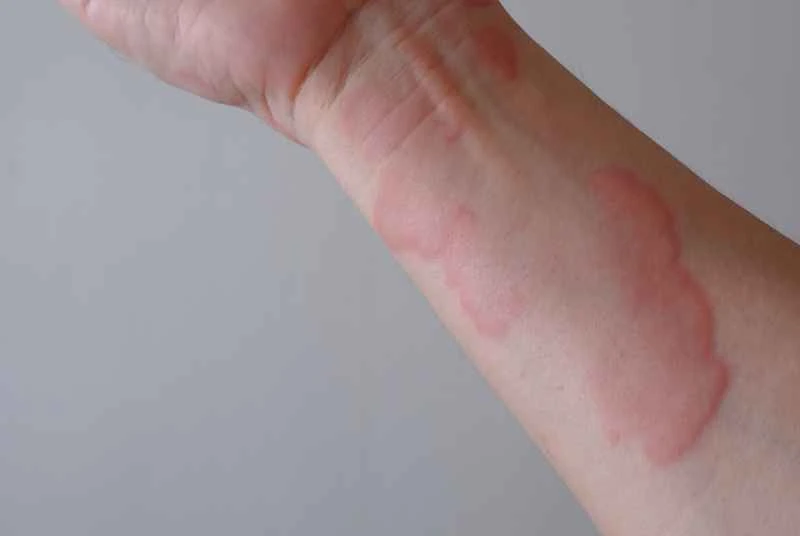
1. **It is not an infectious disease.**
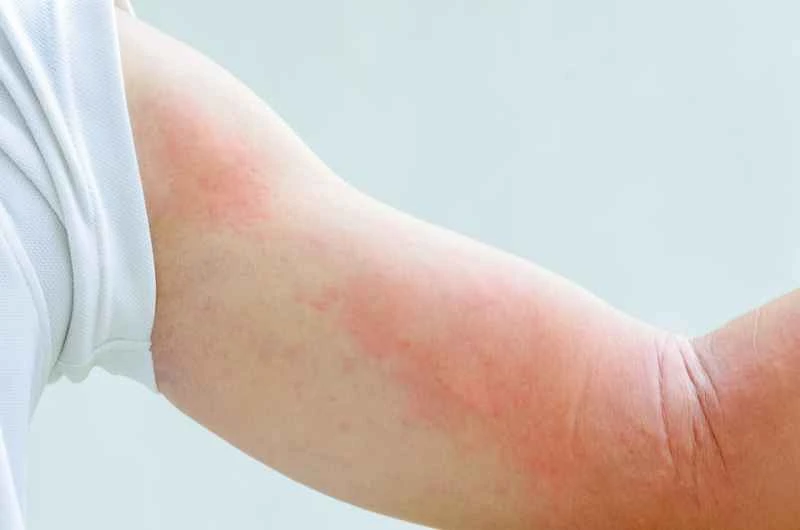
Urticaria (hives) is usually caused by allergies, such as food, pollen, medications, or hot and cold stimuli. It is triggered by the body's internal immune response and is not transmitted to others through contact, respiration, or shared living.
2. **Symptoms and Identification**
The child may develop red or skin-colored wheals, similar to mosquito bites, accompanied by itching. These wheals are not fixed in location and appear and disappear intermittently. Sometimes, swelling of the lips or eyelids may also occur.
3. **Situations Requiring Attention**
Although not contagious, some children may experience difficulty breathing, hoarseness, or difficulty swallowing. If these signs appear, seek medical attention immediately.
To help your child recover better, it's recommended to record any foods or environments they came into contact with before the rash appeared, so your doctor can make a diagnosis. Wear loose-fitting cotton clothing daily to avoid overheating and scratching. Use medication as directed by your doctor; do not adjust the dosage yourself. Keep your home clean and well-ventilated to reduce common allergens such as dust mites. If symptoms recur, consult your doctor about whether allergy testing is necessary.


