Urticaria is not contagious and usually resolves on its own within hours to days. If it recurs frequently, it is recommended to seek medical attention promptly to determine the cause.
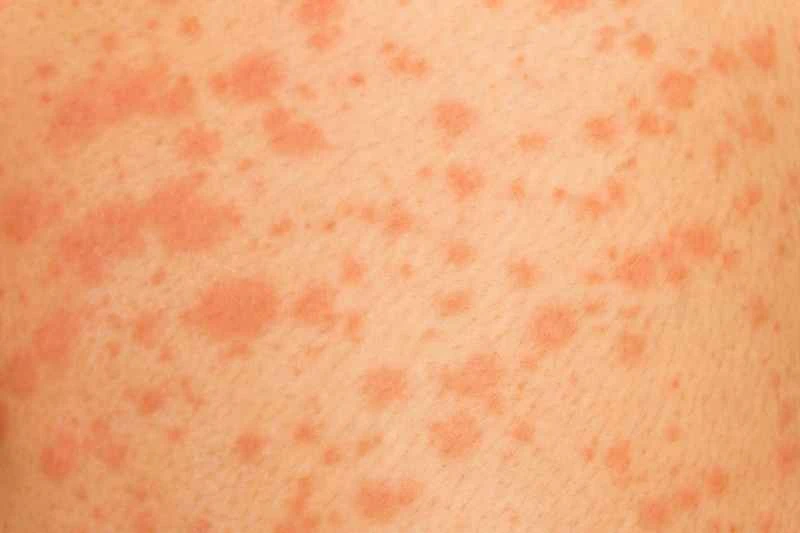
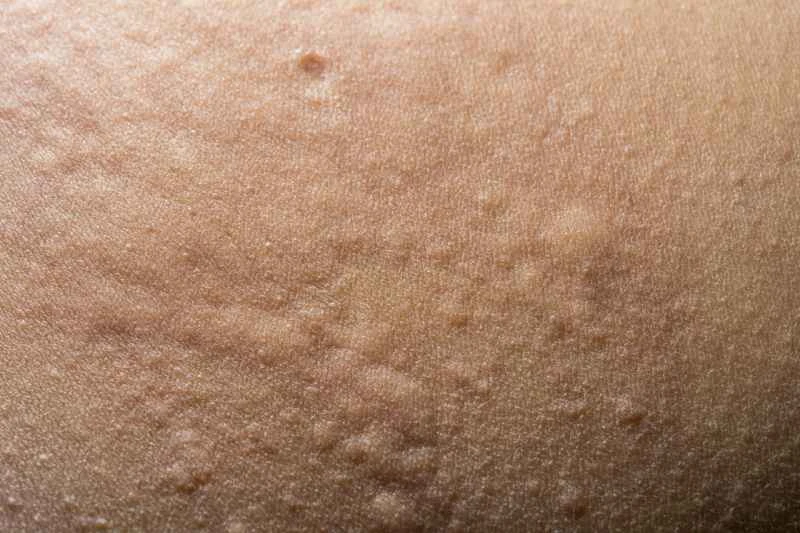
The specific manifestations vary from person to person, and can be mainly divided into two categories:
1. **Acute urticaria:** Usually lasts for hours or days, and most cases disappear gradually within a week. It is often associated with factors such as food, medication, or infection.
2. **Chronic urticaria:** Symptoms recur more than twice a week and last for more than six weeks. Long-term observation and allergen identification are required.
The duration of the disease is affected by a variety of factors:
Individual differences in physical condition may lead to different recovery times.
- Whether or not you are continuously exposed to allergens (such as pollen, pet dander, etc.) can affect the recurrence of symptoms.
- Timely medication or avoiding irritation can help relieve symptoms.
In daily care, it is recommended to record changes in diet and environment to help identify triggers; avoid scratching when itching occurs, and use cold compresses to relieve discomfort; if symptoms persist or are accompanied by abnormalities such as difficulty breathing, please seek medical attention immediately. Maintaining a regular lifestyle and wearing loose cotton clothing can also help reduce flare-ups.


