Urticaria is not contagious, but it can recur. Treatment requires comprehensive management based on the underlying cause. It is recommended to seek medical attention promptly to identify the trigger and receive standardized treatment under the guidance of a doctor.
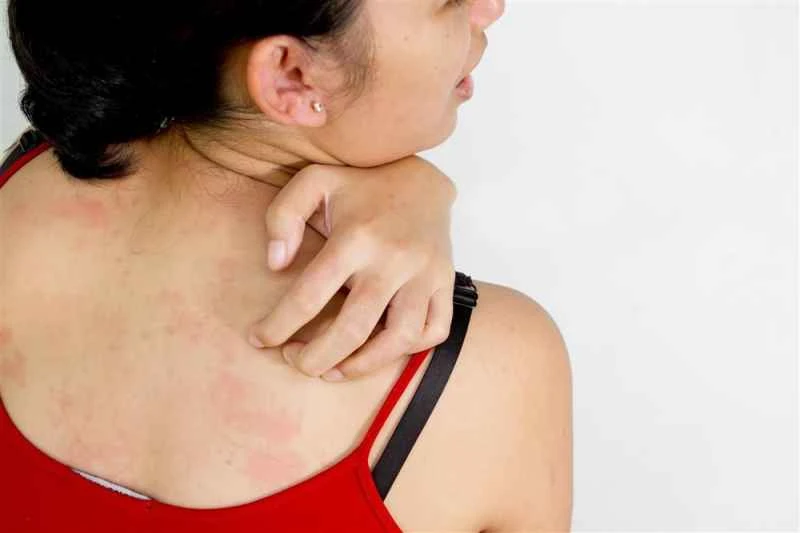
1. **Identify the trigger:** Common causes include food allergies, drug reactions, infections, physical irritants, or psychological stress. Recording your diet and activities before the onset of the attack can help doctors make a diagnosis.
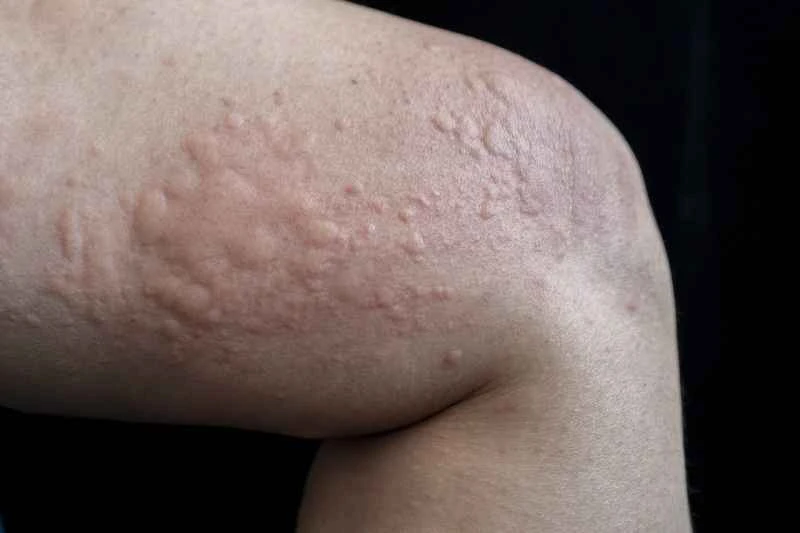
2. **Drug Treatment**: Doctors often prescribe antihistamines to relieve itching and wheals. In severe cases, other medications may be used for a short period of time. It is necessary to strictly follow the medication instructions.
3. **Daily Care**: Wear loose cotton clothing and avoid scratching the skin; bath water temperature should not be too high; reduce spicy food, alcohol and other factors that may aggravate symptoms.
4. **Emergency Treatment:** If severe reactions such as difficulty breathing or dizziness occur, seek medical attention immediately.
In daily life, pay attention to and avoid known triggers, and maintain a regular sleep schedule. If symptoms persist or worsen, please seek medical attention promptly to adjust the treatment plan; do not self-medicate for extended periods.