Treatment for urticaria typically requires selecting an appropriate method based on the specific cause and symptoms. Currently, no single drug can guarantee a complete cure for all patients, but standardized treatment can effectively control and reduce recurrence. It is recommended to improve the condition by combining medication with lifestyle management under the guidance of a doctor.
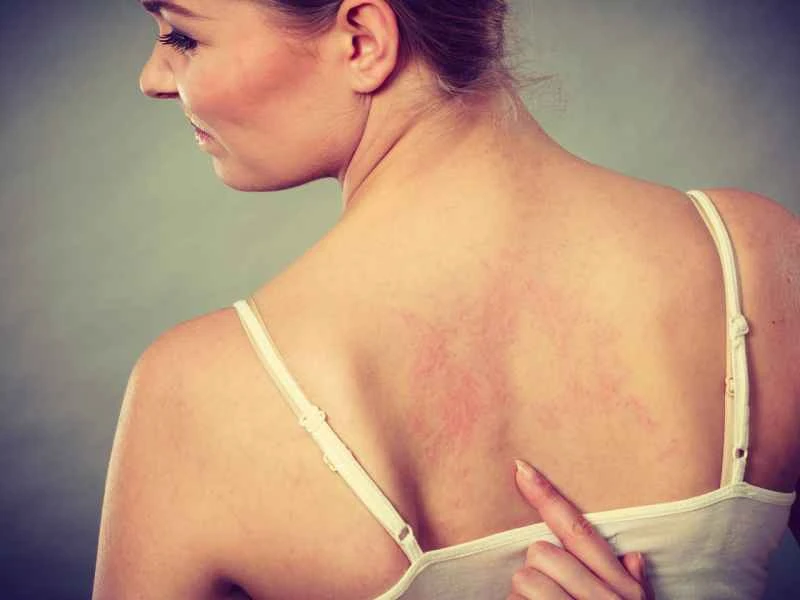

1. **Common Drug Types**
Doctors often prescribe antihistamines, which can relieve itching and wheals. These medications need to be used according to the prescribed course of treatment. For more severe cases, other types of medications may be used for a short period, but it is crucial to strictly follow the doctor's instructions and avoid self-adjustment.
2. **Etiology and Individual Differences**
The causes of urticaria are varied and may be related to environment, diet, or constitution. Before treatment, try recording your diet and activities during an attack to help your doctor determine the cause and prescribe more targeted medication.
3. **Long-term management strategy**
In addition to medication, it's important to avoid known triggers in daily life, such as certain foods, stress, or physical irritants. Keeping your skin clean and wearing loose clothing can also help alleviate symptoms.
In general, treating urticaria requires patience and consistent cooperation. If symptoms recur, it is recommended to have regular follow-up appointments so that the doctor can adjust the treatment plan based on the recovery progress and gradually find a management method that suits you.