Urticaria flare-ups are usually related to allergic reactions, infections, or physical irritants. Currently, there is no guaranteed cure, but with proper treatment and daily management, symptoms can be effectively controlled in most people. It is recommended to seek medical attention promptly to identify the triggers and to cooperate with long-term treatment.
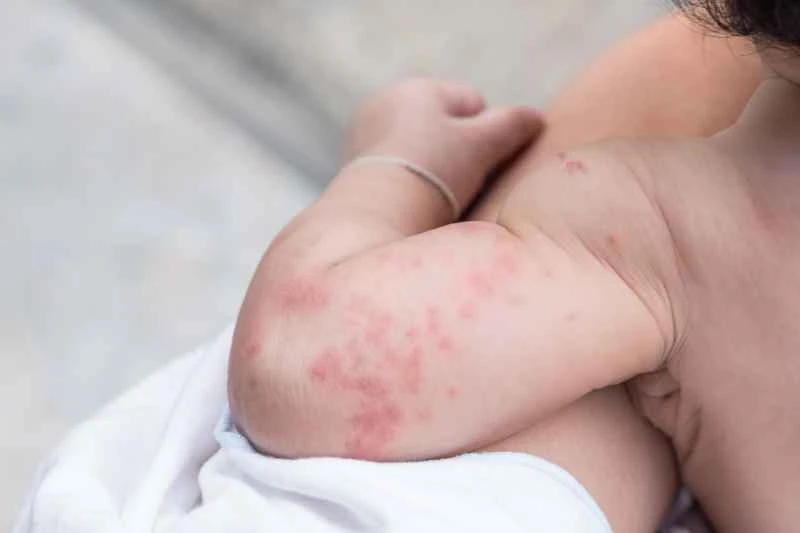
The specific reasons mainly include:
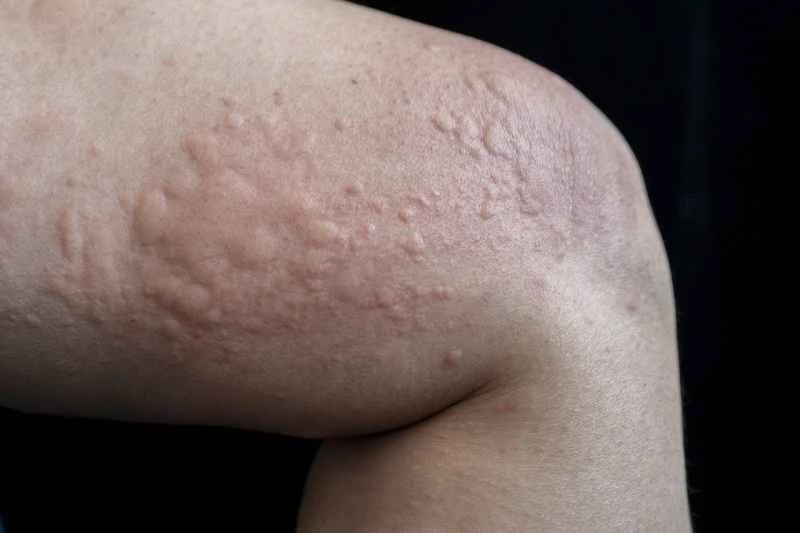
1. Allergens: Foods (such as seafood and nuts), medications, pollen, etc., may trigger an overreaction of the immune system.
2. Effects of infection: Viral or bacterial infections may temporarily trigger skin symptoms.
3. Physical stimulation: Friction, temperature changes, or pressure directly stimulate the skin.
4. Other triggers: Emotional fluctuations and endocrine changes may also contribute to the onset of the disease.
The following aspects should be noted in daily management:
- Record the diet and environment during an attack to help identify potential triggers.
- Avoid scratching your skin and wear loose cotton clothing to reduce friction.
- Use anti-allergy medications under the guidance of a doctor to relieve symptoms, and never stop taking the medication on your own.
If symptoms recur or worsen, it is recommended to have a systematic examination at a dermatology clinic to develop a personalized management plan.