The difficulty of treating recurrent shingles depends on several factors, including an individual's immune status, the frequency of recurrences, and the presence of complications. Shingles is caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), and the initial infection usually manifests as chickenpox, after which the virus remains dormant in nerve tissue. When immunity is weakened, the virus can reactivate, causing a shingles outbreak. Recurrent shingles can be more difficult to treat than the initial outbreak because it often reflects a long-term compromised state of the individual's immune system.
Strategies for treating recurrent shingles include antiviral drugs, analgesics, and immunomodulators. Antiviral drugs such as acyclovir, famciclovir, and varacillovir can effectively suppress viral replication, reduce symptoms, and shorten the course of the disease. Analgesics such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and opioids can help relieve pain. For some patients, especially those experiencing postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), immunomodulators may help improve symptoms. The effectiveness of these treatments may vary from person to person, and recurrent shingles may require a longer treatment period to achieve remission.
There are several potential risks and common misconceptions associated with treating recurrent shingles. Prolonged use of certain antiviral medications can lead to drug resistance, reducing treatment effectiveness. Some patients may mistakenly believe the pain is normal, neglecting the importance of seeking timely medical attention. Those who have experienced postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) may underestimate the long-term effects of this pain, failing to receive appropriate treatment. Understanding these risks and misconceptions is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan.
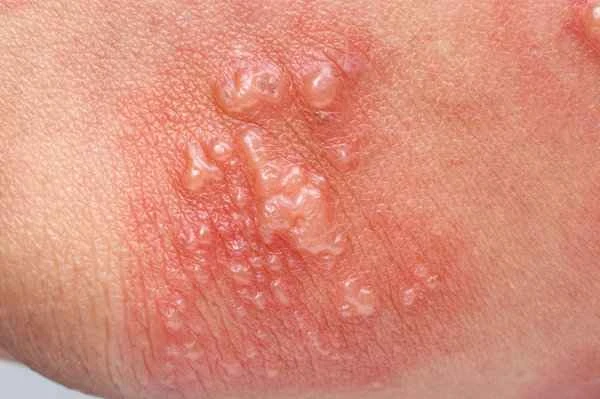
[Management Tip:]
1. Monitor immune function regularly to assess the risk of relapse.
2. Adjust your lifestyle habits to boost your immunity, such as maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise.
3. If pain or other symptoms occur, seek medical attention promptly to prevent the condition from worsening.