Urticaria (hives) is a common allergic skin reaction, typically manifesting as red, itchy welts on the skin. How long it takes for these symptoms to heal depends on the type and cause of the hives, as well as individual differences. Urticaria can be divided into acute and chronic types. Acute urticaria usually resolves on its own within hours to days, while chronic urticaria can last for weeks or even months and is more difficult to cure spontaneously.
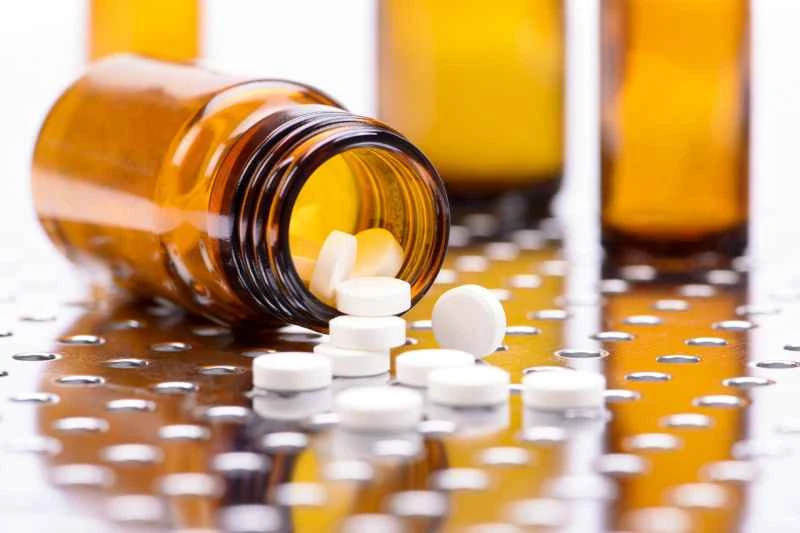
The time it takes for urticaria to heal spontaneously is mainly influenced by its triggers, the course of the disease, and the individual's health condition. Acute urticaria is usually caused by an allergic reaction to food, medication, or environmental factors. In most cases, this type of urticaria will subside spontaneously within hours to days after the trigger is removed. Chronic urticaria is more complex. It may be related to abnormalities in the autoimmune system, chronic infections, or certain chronic diseases. This type of urticaria often takes a long time to heal spontaneously, and in some cases, it may last for months to years, with a lower chance of spontaneous resolution. Treatment and management of chronic urticaria usually require long-term use of antihistamines or other immunomodulators to control symptoms and promote spontaneous remission.

When treating urticaria, it's important to understand that the self-healing time is not fixed but influenced by various factors. While some acute urticaria may resolve spontaneously, this doesn't mean all urticaria will heal naturally. For chronic urticaria, although some patients may experience symptom relief after removing the triggering factor, complete spontaneous remission is unlikely and requires long-term treatment and management. For certain types of urticaria, such as physical urticaria, symptoms may recur under specific conditions; patients need to avoid contact with potential triggers to reduce symptom occurrence.
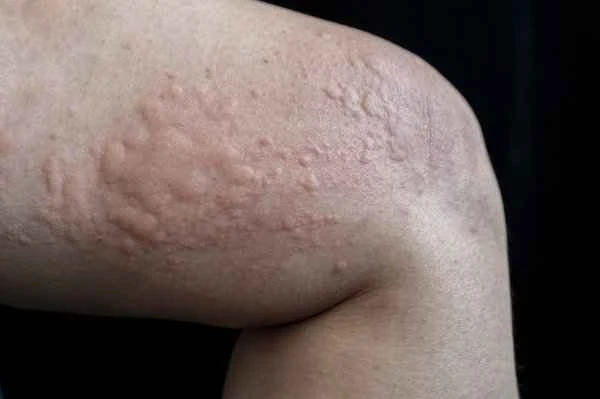
[Management Tip:]
1. Carefully observe and record any food or environmental factors that may trigger urticaria.
2. Maintain good lifestyle habits and avoid excessive fatigue and mental stress.
3. If persistent or recurrent urticaria occurs, seek medical attention promptly for targeted treatment.


