Treatment for refractory urticaria involves a comprehensive approach combining medication, lifestyle modifications, and avoidance of triggering factors to control symptoms and reduce the frequency and severity of attacks. Refractory urticaria is defined as urticaria that does not respond well to conventional treatments, has prolonged symptoms, and recurs frequently. The core of treating refractory urticaria lies in identifying and avoiding triggering factors, using antihistamines to control symptoms, and, when necessary, using immunosuppressants or biologics to modulate the immune response.
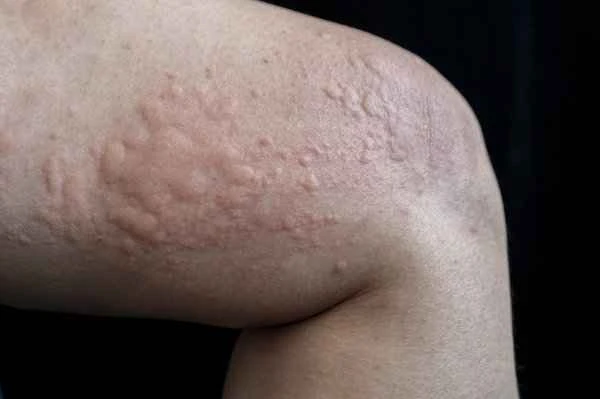
When treating refractory urticaria, the first step is to identify the triggering factors, including food, medications, and environmental factors, and to avoid contact with these factors as much as possible. Antihistamines are the first-line drugs for controlling symptoms; they can effectively relieve symptoms such as itching and redness. If antihistamines are ineffective, immunosuppressants or biologics can be considered. These drugs reduce symptom flare-ups by modulating the immune system. Patients also need to pay attention to adjusting their diet and lifestyle, such as avoiding foods that may trigger symptoms, maintaining good sleep quality, and avoiding excessive fatigue.
During the treatment of refractory urticaria, patients may encounter some risks and misconceptions. Over-reliance on medication while neglecting lifestyle adjustments can lead to recurrent symptoms. Some patients may stop taking medication on their own after symptom relief, which can cause a rebound in symptoms or even worsen the condition. Patients need to follow their doctor's instructions, attend regular follow-up appointments, and adjust their treatment plan promptly during the treatment process.
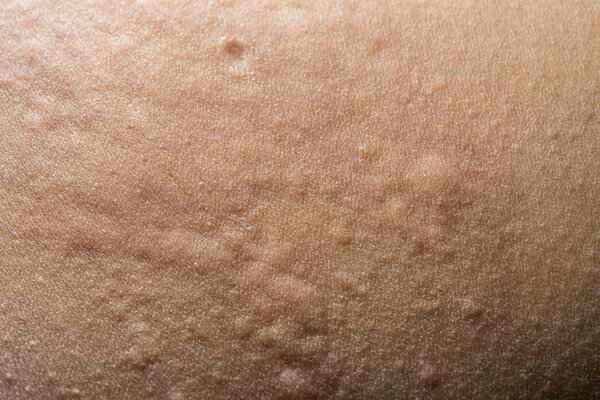
[Management Tip:]
1. Regular follow-up visits are necessary to monitor changes in symptoms and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
2. Pay attention to dietary control and avoid known triggering factors.
3. Maintain good lifestyle habits and avoid excessive fatigue and mental stress.
4. Seek medical attention promptly if symptoms worsen or new symptoms appear.


