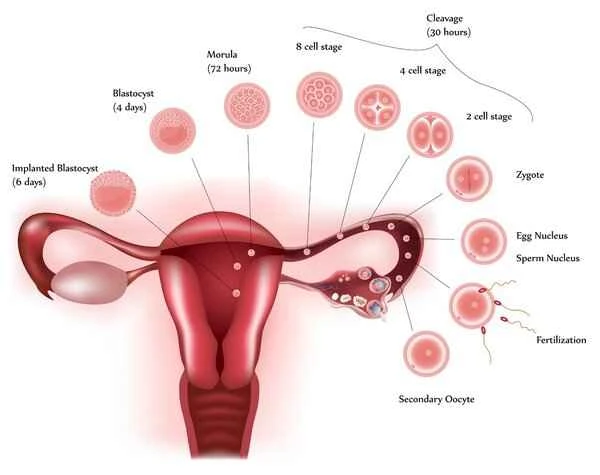
Implantation on a scar means that the embryo implants in scar tissue left by a previous surgery or trauma. This situation requires special attention because it can affect the successful completion of the pregnancy.
When implantation occurs on scar tissue, this location can increase the risk of uterine rupture, especially in women with scarred uteruses following cesarean sections. Scar tissue typically has less elasticity and blood supply than normal uterine tissue, which can lead to unstable embryo implantation and increase the risk of miscarriage or premature birth. For women with scarred uteruses, doctors usually recommend closer pregnancy monitoring and management to ensure the safety of both mother and baby.
When dealing with implantation on a scar, doctors consider a range of factors, including the scar's location, size, shape, and the patient's overall health. Treatment strategies may include regular ultrasound examinations to monitor the health of the uterus and embryo, and potential medications to prevent or manage complications. Each case is unique, so doctors will develop a personalized management plan based on the specific circumstances.
[Management Tip:]
1. Have regular ultrasound examinations to monitor embryonic development and the condition of uterine scars.
2. Follow your doctor's advice; medication may be needed to prevent or treat potential complications.
3. Maintain healthy lifestyle habits, including a balanced diet and moderate exercise, to support a healthy pregnancy.
4. If any abnormal symptoms occur, such as abdominal pain or vaginal bleeding, seek medical attention immediately.


