Breaking a keloid can lead to infection, increased inflammation, and delayed healing. A keloid is an overgrowth of scar tissue, typically hard and raised. Breaking it not only disrupts its integrity but can also impair the skin's barrier function, making it easier for bacteria to invade and increasing the risk of infection.
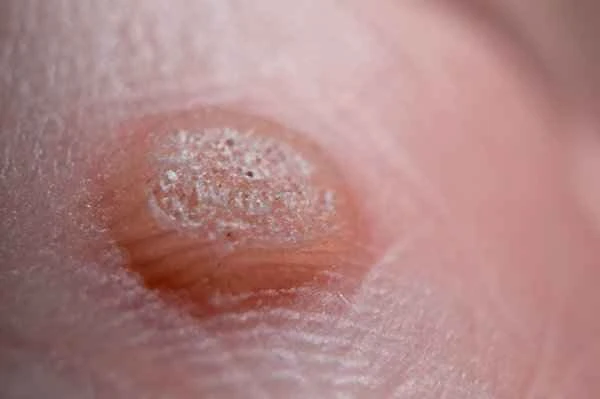
If a keloid scar is broken, the fibrous tissue inside may be exposed to air, which can not only cause pain but also exacerbate the inflammatory response. In this case, the keloid scar may become more red and swollen, accompanied by localized heat and increased pain. Improper treatment may also affect the normal healing process of the wound, leading to prolonged healing time or even the formation of new keloid scars.
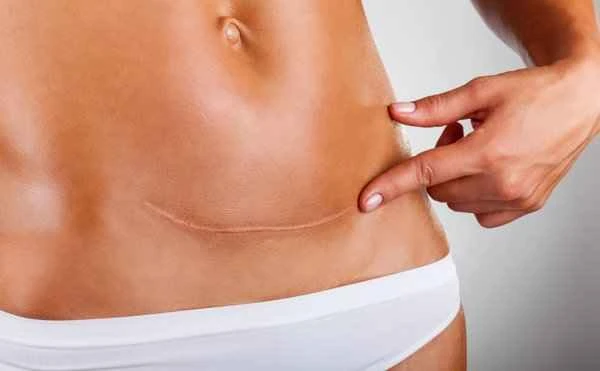
When treating keloids, never break them or irritate their surface yourself, as this can not only cause infection but also worsen the keloid. The correct approach is to keep the wound clean, avoid friction and irritation, and seek professional medical help if necessary.

[Prevention Tips:]
1. Keep the keloid area clean and dry.
2. Avoid applying unnecessary pressure or friction to keloids.
3. Use doctor-recommended scar care products regularly, such as silicone sheets or gels.
4. Carefully observe changes in keloid scars; seek medical attention promptly if any abnormalities are observed.


