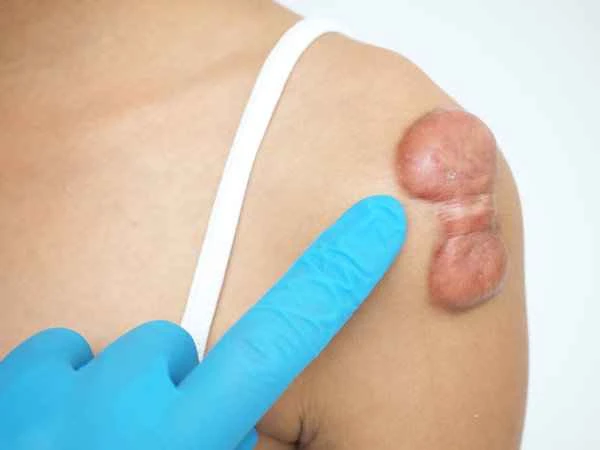
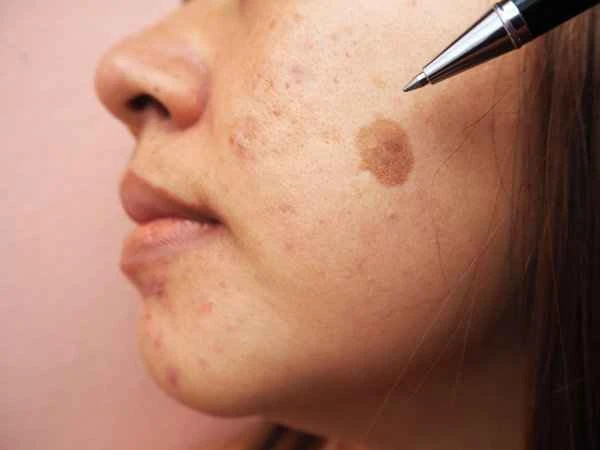
The goal of treating condyloma acuminata is to completely eliminate the virus and prevent recurrence. Condyloma acuminata is a skin lesion caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. Treatment of condyloma acuminata not only involves eliminating the visible warts but also clearing the virus as much as possible to reduce the risk of recurrence.
The core principle of treating genital warts is to eliminate the virus and the warts through physical, chemical, or immunotherapy. Physical therapies include cryotherapy, electrocautery, and laser treatment. These methods can directly remove the warts, but they may not completely eliminate the virus, thus carrying the risk of recurrence. Chemical therapies use topical medications such as salicylic acid and fluorouracil. These medications can disrupt the viral replication process, but like these, they cannot guarantee complete elimination of the virus. Immunotherapy works by strengthening the body's immunity to fight the virus, such as using immunomodulators or getting the HPV vaccine. These methods can reduce viral replication and spread, thereby lowering the risk of recurrence.
During the treatment of genital warts, patients may encounter some misconceptions, such as believing that the disappearance of the warts means the virus has been eliminated, or that genital warts are a minor problem that does not require special treatment. In reality, the treatment of genital warts requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors, including the type of virus, the severity of the infection, and the patient's immune status. It is also necessary to be aware of some potential risks during treatment, such as pain, infection, and scarring. Therefore, choosing the appropriate treatment method and doctor is crucial.
[Management Tip:]
1. Regularly perform HPV testing to monitor viral load.
2. Adjust your lifestyle habits to enhance your immunity.
3. If new warts appear or existing warts enlarge, seek medical attention promptly.