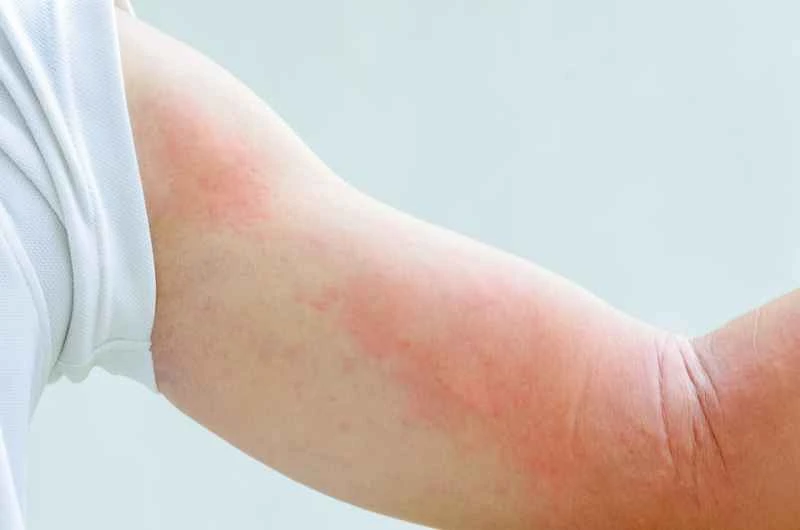
Shingles is a disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which usually causes a painful rash on the skin, but can sometimes also affect the throat.
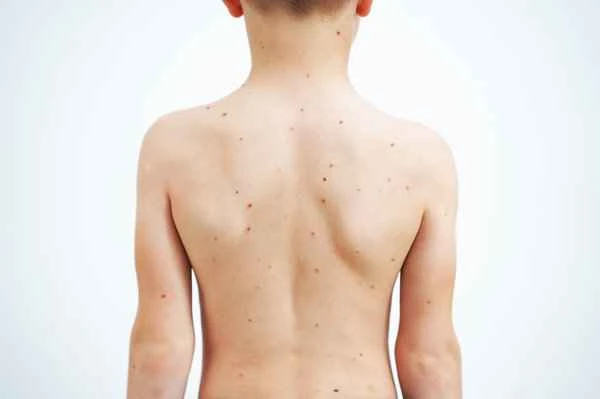
Shingles typically begins with pain, itching, or abnormal sensations, followed by redness and blisters. The virus usually affects one side of the body, with a rash appearing along the nerve distribution area. Shingles primarily affects the skin, but it can also affect the throat, causing a sore throat. This pain is usually due to the virus affecting the nerves in the throat. While shingles rarely affects the throat, if it does, patients may experience severe throat pain, which can affect swallowing and speaking.
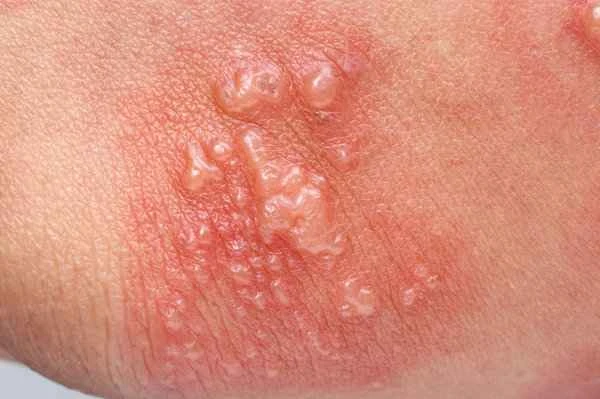
While it's rare for shingles to affect the throat, it can cause significant discomfort when it does occur. The pain of shingles may not be limited to the skin but can also involve nerves, leading to a sore throat. This pain may be due to the virus directly attacking the nervous system. Even though shingles primarily manifests as skin symptoms, its impact on other parts of the body should not be ignored. Shingles can also cause other complications such as eye infections and hearing loss. Therefore, timely medical attention and appropriate treatment are crucial for shingles patients.
[Management Tip:]
1. Seek medical attention promptly and receive antiviral treatment.
2. Get plenty of rest and avoid overexertion.
3. Maintain good personal hygiene habits to avoid the spread of the virus.