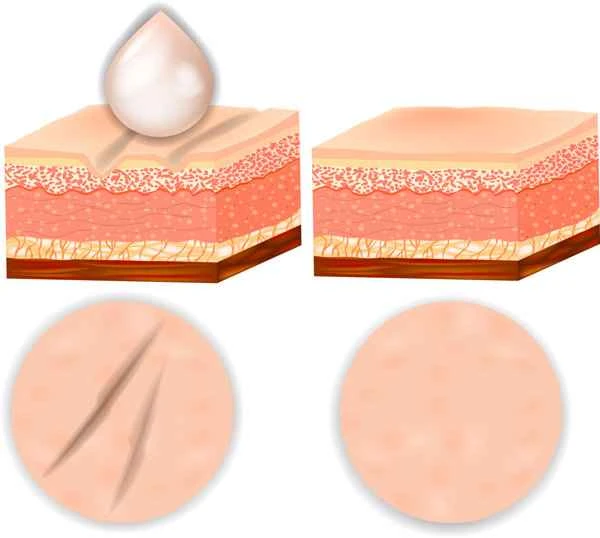
Urticaria (hives) is mainly related to allergic reactions. When the body comes into contact with certain substances or is stimulated, the immune system releases substances such as histamine, leading to red, swollen, and itchy wheals on the skin. Treatment involves relieving symptoms with medication and identifying the triggering factors. The following is a detailed explanation:
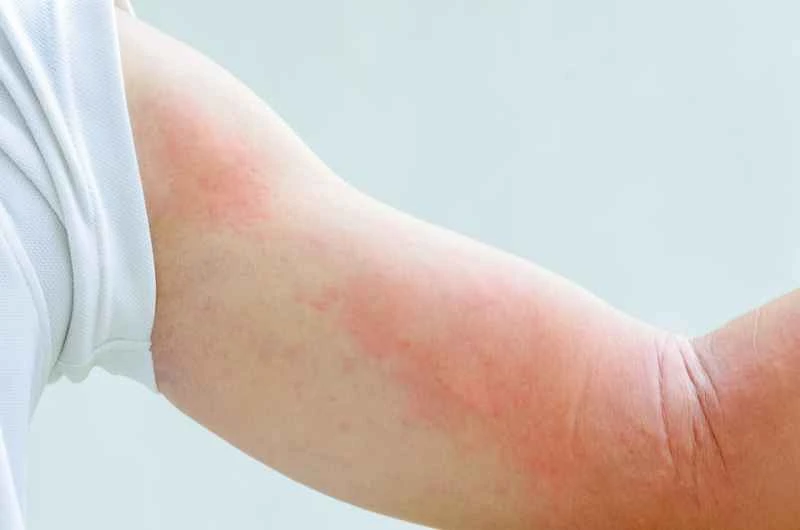
1. Common triggers: Foods such as seafood and nuts, medications such as penicillin, and environmental factors such as pollen and dust mites can trigger allergies. Infections, stress, or temperature changes can also trigger them.
2. Symptom characteristics: red or skin-colored wheals of varying sizes suddenly appear on the skin, accompanied by significant itching. They usually subside on their own within 24 hours, but may recur.
3. Treatment: Doctors often recommend antihistamines to relieve itching and redness. If symptoms are severe, other medications may need to be used for a short period, but it is essential to strictly follow the doctor's instructions.
We suggest you keep a record of your daily diet and environmental exposures to help identify triggers; avoid scratching during an attack, and you can use cold compresses to relieve discomfort. If the rash persists or is accompanied by difficulty breathing, please seek medical attention promptly.