Urticaria is generally not considered a serious illness, but its severity depends on the specific circumstances. In most cases, it is not life-threatening, but it can affect quality of life. It is recommended to seek medical attention promptly to determine the cause and manage the condition appropriately.
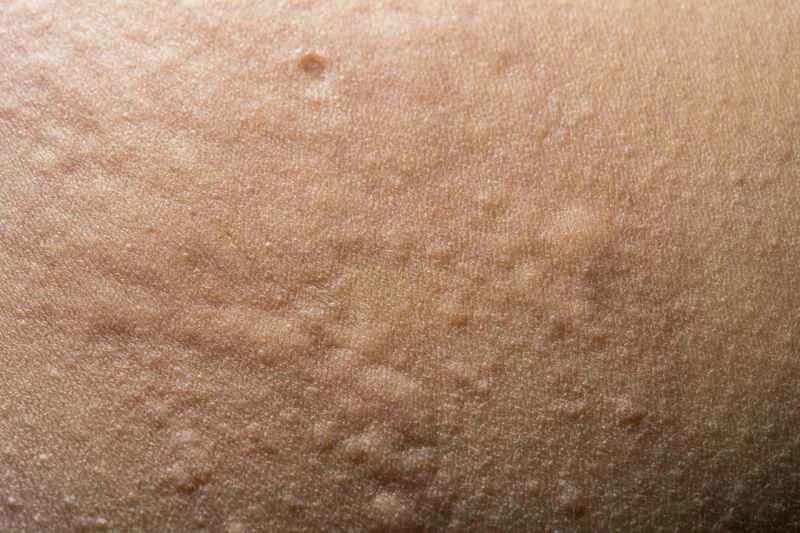
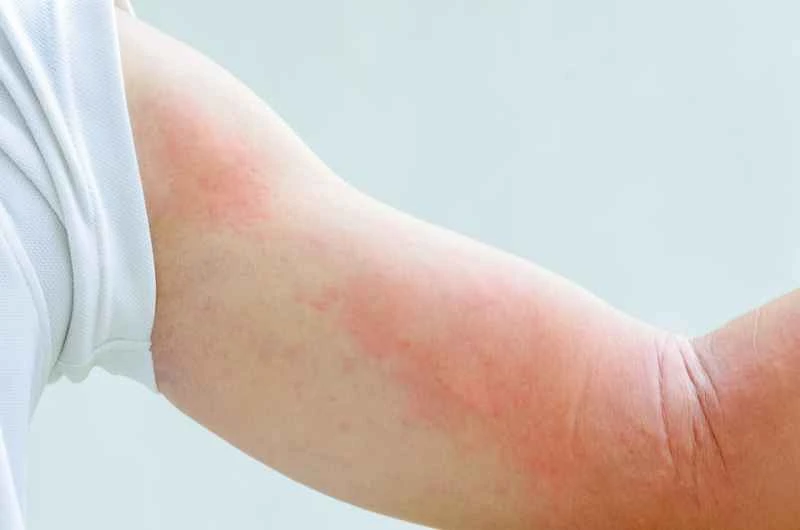
1. Common symptoms: Urticaria is mainly characterized by red or skin-colored wheals on the skin, accompanied by itching. The symptoms may vary in severity and usually subside on their own within 24 hours.
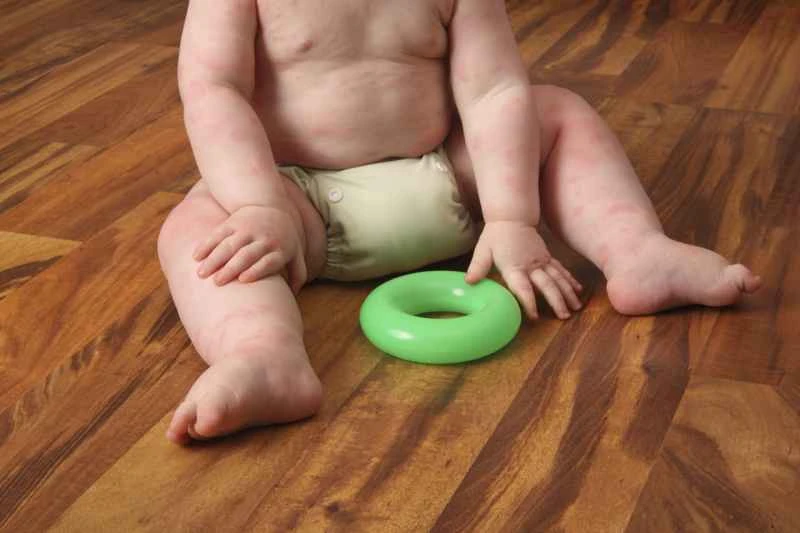

2. Triggering factors: Food, medication, infection, temperature changes, or stress can all be triggers, and some patients may not be able to find a clear cause.
3. Warning signs: If accompanied by symptoms such as difficulty breathing, tightness in the throat, dizziness, or abdominal pain, it may indicate a serious reaction and requires immediate medical attention.
4. Differences in disease course: Acute urticaria usually improves within a few weeks, while chronic urticaria may recur for more than six weeks and requires long-term management.
Daily advice includes keeping a record of your diet, activities, and environment during flare-ups to help your doctor identify triggers; avoid scratching your skin and wear loose-fitting cotton clothing; use medication to control symptoms under the guidance of your doctor, and do not self-medicate for extended periods. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and a calm state of mind can also help reduce flare-ups.