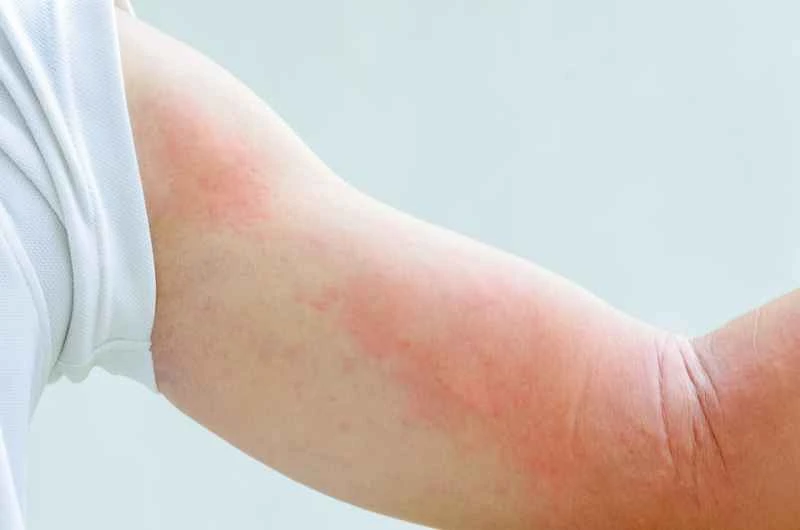
Urticaria (hives) is a common allergic skin reaction, and its rapid resolution hinges on timely identification of the trigger and effective treatment. Urticaria is usually associated with allergens such as food, medications, and environmental factors. These factors lead to elevated histamine levels in the body, resulting in symptoms like redness, swelling, and itching. To quickly resolve urticaria, it's essential to first identify and avoid contact with potential allergens, while simultaneously using antihistamines to lower histamine levels and alleviate symptoms. Cold compresses and avoiding hot baths can also help relieve itching and reduce skin inflammation.
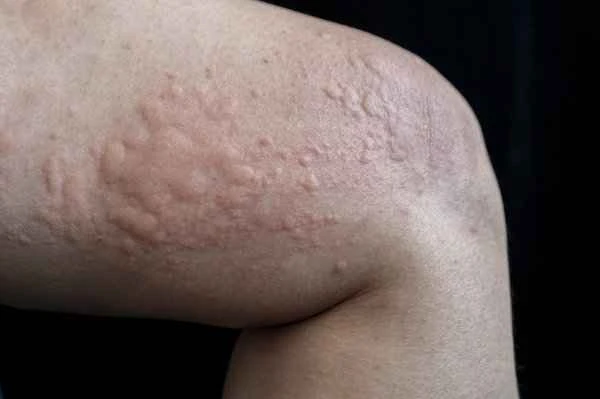
During the treatment of urticaria, patients may encounter some misconceptions. For example, some patients may mistakenly believe that urticaria is permanent and neglect the importance of seeking timely medical attention. In reality, the duration of urticaria is closely related to individual differences, the nature of the allergen, and the timeliness and effectiveness of treatment. For the treatment of urticaria, over-reliance on over-the-counter medications should be avoided. Instead, antihistamines and other possible treatments should be used rationally under the guidance of a doctor. At the same time, self-diagnosis and self-treatment should be avoided to prevent delaying the condition or causing unnecessary side effects.
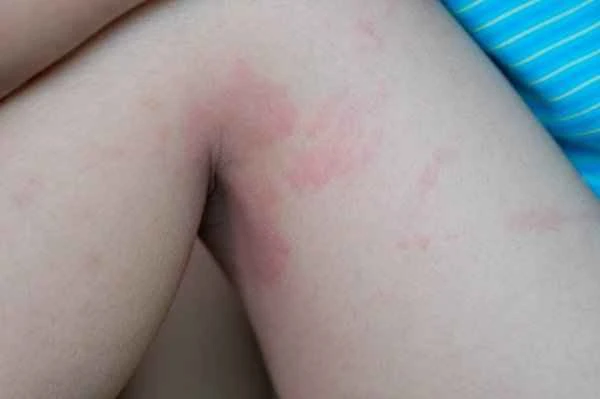
[Management Tip:]
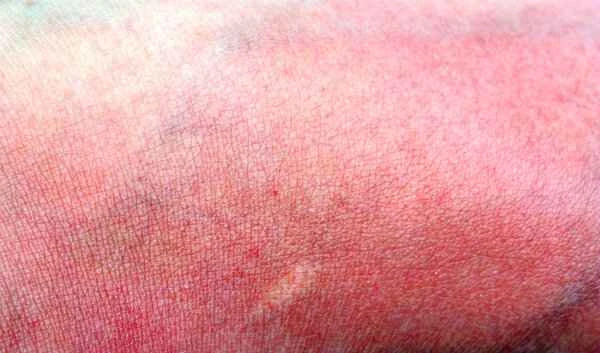
1. Identify and avoid contact with potential allergens as soon as possible.
2. Use antihistamines appropriately under the guidance of a doctor.
3. Keep skin clean, avoid hot baths, and use cold compresses to relieve itching.
4. If symptoms persist or worsen, seek medical attention promptly.