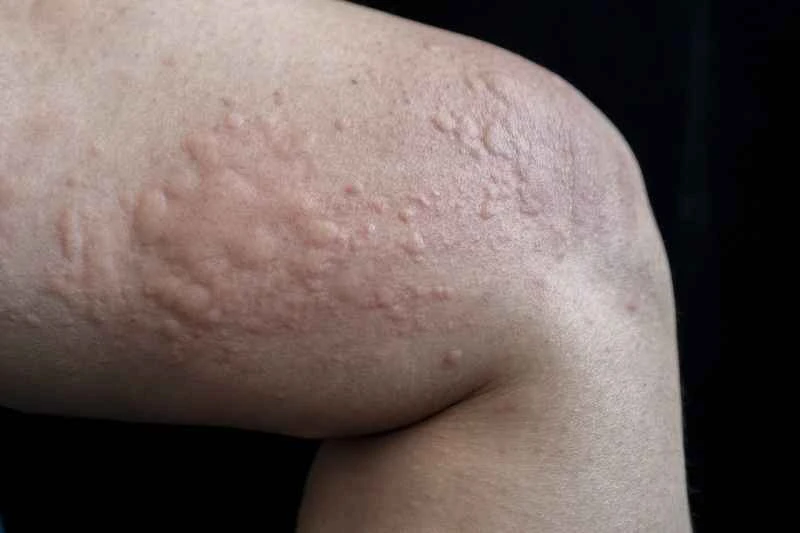
During an acute urticaria attack, topical medications such as calamine lotion or mild steroid creams can be used as prescribed by a doctor to help relieve symptoms. However, oral antihistamines are usually required to control the condition more quickly.
1. Selection of topical medications
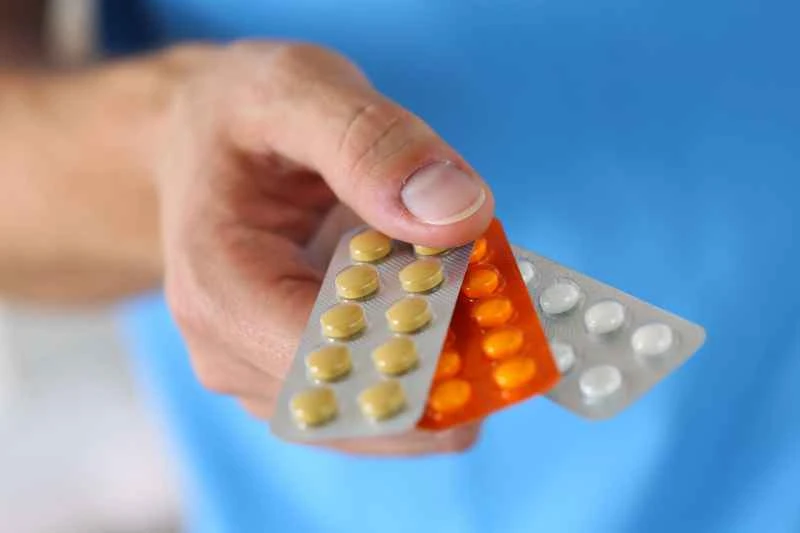
Calamine lotion has astringent and antipruritic properties, and can temporarily relieve skin itching after application. If the rash is significantly red and swollen, the doctor may recommend short-term use of a mild steroid cream, but attention should be paid to the duration and application site to avoid long-term, large-area application.
2. Core Treatment Methods
Topical medications primarily relieve surface symptoms, while oral antihistamines are often required for the fundamental treatment of acute urticaria. These medications suppress allergic reactions and reduce wheal flare-ups from within. Specific medication use should be determined by a doctor based on the individual's condition; medication should not be used or discontinued arbitrarily without medical advice.
3. Key Points of Auxiliary Nursing Care
During medication, avoid scratching the skin and wear loose cotton clothing to reduce friction. Also, keep a record of factors that may trigger urticaria, such as food and environmental changes, to help prevent recurrence.
If the rash spreads rapidly or is accompanied by severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing or dizziness, please seek medical attention immediately. Maintaining skin cleanliness, avoiding known allergens, and using medication as directed by a doctor will better promote recovery.


