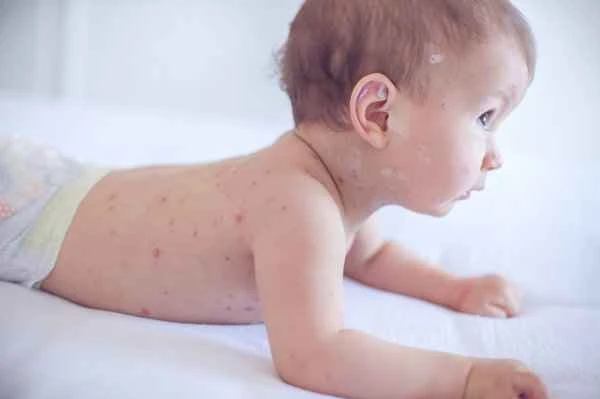
Injection treatment may be effective for some stubborn cases of urticaria, but the decision depends on the specific type and the doctor's assessment. It is generally recommended to try conventional medications first.
1. When is injection appropriate? For chronic urticaria that does not respond well to conventional oral medications and recurs frequently, doctors may consider injection therapy, such as using antihistamines or biologics, to help relieve stubborn symptoms.
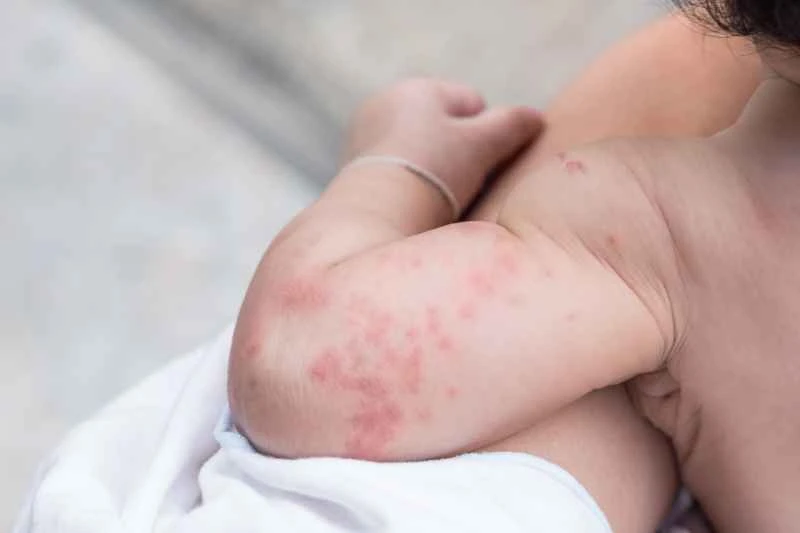
2. Results vary from person to person: Injections are not effective for everyone. The reaction is related to the cause of urticaria and individual constitution. Some people may experience a reduction in symptoms, while others may not see significant results and may require multiple treatments.
3. Be aware of potential limitations: Injection therapy is usually a second-line option and should be performed under the supervision of a doctor. There may be local reactions or high costs, so it is not advisable to try it on your own.
It is recommended to consult a dermatologist first to determine the type of urticaria through examination. If conventional medications are difficult to control, you can discuss the feasibility of injections with your doctor. At the same time, record the pattern of flare-ups, avoid known triggers (such as food, stress, etc.), and comprehensive management is more conducive to long-term stability.